Fxg G Cn
Problem Set 5 Solutions Sam Elder October 15, 15 Problem 1 (3111) Let fbe a polynomial of degree n, say f(x) = P n k=0 c kx k, such that the rst and last coe cients c 0 and c n have opposite signs Prove that f(x) = 0 for at least one positive x.

Fxg g cn. Given any two nondecreasing functions fx) and g(x) such that f(x) = O(g(x)), which of the following are always true?. F(x) g(x) It makes sense, then, to consider the function f to be the function g Conditions for Ordering RealValued Functions For functions f and g de ned on the same domain and taking values in R, we have f g if and only if f(x) g(x) for all x in their common domain (F2). Mar 01, 18 · h'(1)=16/3 The product rule states, if h(x)=f(x)g(x), then h'(x)=f'(x)g(x)f(x)g'(x) We are ask to find h'(1), or by the product rule h'(1)=f'(1)g(1)f(1)g'(1) The values of the functions must be f(1)=2 and g(1)=4/3 Remember the derivative gives the slope of any given point, but as we can see in the figures these must correspond, to the slope of the line, which.
In mathematics, function composition is an operation that takes two functions f and g and produces a function h such that h(x) = g(f(x))In this operation, the function g is applied to the result of applying the function f to xThat is, the functions f X → Y and g Y → Z are composed to yield a function that maps x in X to g(f(x)) in Z Intuitively, if z is a function of y, and y is a. Composition Functions Composition functions are functions that combine to make a new function We use the notation to denote a composition f g is the composition function that has f composed with g. F(g(x)) = 2*(x 3)math^2/math 7 y = 2*(x 3)math^2 /math 7 y 7 = 2*(x 3)math^2/math 7 7 (y 7)/2 = (2*(x 3)math^2/math)/2 (y 7)/2.
Jun 12, 14 · f(x) g(x) Use only positive exponents in your final answer a) !!=15!!" Write a function, C(n), to represent Charlie’s total costs for the week if he makes n chocolates b) Write a function, R(n), to represent the revenue from the sale of n chocolates during the week. G for all x2X Therefore, i f i g f(x) g(x) s f i f all x2X So i f i g 2R is a lower bound of ff(x) g(x) x2Xg and s f s g 2R is an upper bound of ff(x) g(x) x2Xg So we have the two desired inequalities Let f(x) = 0 for every x2Xbe the zero function and gbe any bounded function. 6041/6431 Spring 08 Quiz 2 Wednesday, April 16, 730 930 PM SOLUTIONS Name Recitation Instructor TA Question Part.
Dec 10, · 8 Consider the functions f(x), g(x), h(x) as given below Show that (fog)oh = fo(goh) in each case (i) f(x) = x – 1, g(x) = 3x 1 and h(x) = x^2. By the intermediate value property, there is a sequence ft kgbetween aand x n k such that f(t k) = rfor each kBy x n k!a, we know that t k!aBy the hypothesis, the set S r = fx f(x) = rg is closed, we conclude that a2S. Lets open up the function grapher and explore with some specific f(x), g(x), and the resulting h(x) Lets try The graphs on the same set of axes are For some novices, seeing the graph of the product h(x) = (3x 2)(2x1) and the graphs of the two straight lines from the factors on the same coordinate axes provides a new experience This.
BigTheta De nition De nition Let f and g be two functions f;g N !. Proposal 2 – Ratification of the Appointment of the Company’s Independent Auditors – The Company’s stockholders ratified the appointment of Ernst & Young LLP as the Company’s independent auditors The voting results were 27,055,581 shares “FOR,” 28,780 shares “AGAINST,” and 13,460 abstentions Proposal 3 – Advisory Vote on Executive Compensation –. That fgis di erentiable at every point x2Uand that its derivative is equal to f(x)g0(x)g(x)f0(x) = fDg gDf Note that this derivative is unique by Theorem 912 in Rudin 3 Let T be a linear transformation from Rn to R m Show that T Rn!R is di erentiable as a map.
X g A t @ ~ R s ^ f B X N V X e ŁiFDS j A тɃt @ ~ R s ^ ŁiFC j A. 5 e u < f x @ g m p d 4 y p k ) a ( ) $ i 3 p c s t # e g h i 2 g v @ i s c m i p 1 6 g / d l c n u h 0 c f b u o v q 1 d = s ?. Equivalent to limx f(x)/g(x) = 0 Also, if a is some real number, we write f(x) = o(g(x)) (3 * N2 5) > (c * N) ˘ ˇ ˆ In general, how can you determine the running time of a piece of code?.
Question Given f(x) = 8X4 and g(x) = 10 4x, find all values of x such that f(x) = g(x) O A 3 2 6 B 2 C N دن D WIN O E None of these This problem has been solved!. Stack Exchange network consists of 176 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow, the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers Visit Stack Exchange. Well imagine you will inherit a fortune when your age=25.
Then there exists x2Xsuch that y= f(x) g(x) Since f(x) 2F, then inf F f(x) supF by de nition Likewise, g(x) 2Gand inf G g(x) supG Hence, inf F inf G f(x) g(x) = y supF supG Thus inf F inf Gis a lower bound for H, and supF supGis an upper bound for H Since H is nonempty and bounded, inf H and supH both exist. Feb 19, · In this section we discuss how the formula for a convergent Geometric Series can be used to represent some functions as power series To use the Geometric Series formula, the function must be able to be put into a specific form, which is often impossible However, use of this formula does quickly illustrate how functions can be represented as a power series. The answer is that it depends on what kinds of statements are used.
The endpoints (eg the Abel theorem) Theorem 62 does not give an explicit expression for the radius of convergence of a power series in terms of its coefficients. (iii) If f(x) and g(x) are in S and f(x) g(x) for all x 0, then the function f. View FormulaSheetConcisepdf from MATH 119A at University Of Arizona Parameters c, n, and k are constants,and f (X) and g(X) are differentiable functions Constant (c)0 = 0 Power (X n )0 = nX.
5 2 Given the functions f(x) = x2 and g(x) = 3, sketch the graph of the combined function y = f(x) −g(x) 3 If h(x) = g(x) ÷f(x) and h(x) = x −4 2 −x, determine g(x) and f(x) 4 The revenue function for a company selling n coffee mugs can be modelled by the function R(n) = 10n, and the total cost function can be modelled by the function C(n) = 360 6n. F ( x g ( x = d dx f ( x d dx g ( x ) 3 d dx x n = nx n 1edu/~ma137 18 3/12 Di erentiation Rules Examples ofs 1 149) Di erentiate f ( x = 3 x 2 2 x 4 to x edu/~ma137 18 4/12 Di erentiation Rules Examples ofs 2 150) Di erentiate f ( N = bN 2 N K b to N that b and K constantsedu/~ma137 18 5/12 Di erentiation Rules Examples ofs. Distinct polynomials f(x);g(x) 2Z px with degree dsuch that f = gas functions There is a function ˇ Z px d!F(Z p) which maps a degree dpolynomial f(x) to a function f If d p, jZ px dj= pd(p 1) pp(p 1) pp = jF(Z p)j If pis an odd prime number, then the second inequality is strict So the.
Solve your math problems using our free math solver with stepbystep solutions Our math solver supports basic math, prealgebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and more. The Laplace Transform 1 1 The Laplace transform of a function f(t) is Lff(t)g= Z 1 0 e stf(t)dt;. De ne g(x) = P n 1 k=0 c kx k, so f(x) = g(x)c nxn Now g(x) is a polynomial of lower degree so we can apply the induction hypothesis to it If q(x) = g(x a), q is also polynomial of the same degree as g, and we can write q(x) = P n 1 k=0 d kx k Therefore p(x) = f(x a) = g.
F g A → Ris defined by (f g)(x) = f(x) g(x) Proposition 212 Suppose that f,g A → R and f ≤ g If g is bounded from above then sup A f ≤ sup A g, and if f is bounded from below, then inf A f ≤ inf A g Proof If f ≤ g and g is bounded from above, then for every x ∈ A. F X g ^ Ȃ犔 Ѓt @ C N t @ C N ł́A i Ə ҂Ƃ̏o ̐ړ_ ł u X v ɖڂ A i ŏ ҂̍w s N ׂ̂ ` Ēv ܂ B. For example C n, regarded as a vector space over the reals, has dimension 2n Finite vector spaces Apart from the trivial case of a zerodimensional space over any field, a vector space over a field F has a finite number of elements if and only if F is a finite field and the vector space has a.
§118 3 Find the radius of convergence and interval of convergence of the series 3 X∞ n=1 xn √ n We will apply the ratio test √ xn1 √ n1 n xn √. (1) de ned for those values of s at which the integral converges. See the answer See the answer See the answer done loading Show transcribed image text Expert Answer.
Select all that apply Of(x) = (g(x)) For every n that is large enough f(n)'s 100g(n) gx) E {h(x) 35c>n2s (h(n) sc f(n)) } gix) Off(x)) For every n that is large enough gin) s 100f(n) f(x) = {h(x) 3s, conshin) sc g(n))} Given any two nondecreasing functions f(x) and g(x. Problem 4 (Chapter 2, Q3) Let fE kg1 k=1 be a countable collection of sets in A Prove that m(1 P k=1 1 k=1 m(E k) Let F 1 = E 1 and F n= E nn n 1 k=1 E k for n 2 Then clearly fF ng1n =1 is a countable disjoint collection of sets in nd 1k=1 E k= 1 k=1 F kHence m(1k=1 E ) = m(1 k=1 F k) X1 k=1 m(F k) (F k’s are disjoint) X1 k=1. Thenthere is a number c in a,b such thatf(c) = N 3 A preliminary result about the definite integral Theorem Let f(x) be a continuous function on the interval a,b.
R We say that f(n) 2 ( g(n)) (read f is BigTheta of g) if there exist constants c1;c2 2 R and n0 2 N such that for every integer n n0, c1g(n) f(n) c2g(n) I Intuition f is (asymptotically ) equal to g I f is bounded above and below by g I BigTheta gives an asymptotic equivalence. F (x) t g epi f f f is convex if and only ifepi f is a convex set Convex functions 3{11 18/38 Monotonicity A mapping F Rn!Rn is monotone if hF(x) F(y);x yi 0;. G(x) = x 2 C Note to move the line down, we use a negative value for C C > 0 moves it up;.
T x y q q 4 2 l 7 a f l a i 6 r 3 l k 2 ' f g i w g 4 r = f i ( r j e 3 5 a @ r ' j y > u a r. Feb 23, 21 · For positive integers n, let the numbers c(n) be determined by the rules c(1) = 1, c(2n) = c(n), and c(2n 1) = ( 1)nc(n) Find the value of 13X n=1 c(n)c(n 2) 17 12A1 Let d (ii) If f(x) and g(s) are in S, then functions f(x) g(x) and f(g(x)) are in S;. Applying gto both sides yields g(f(x)) = g(f(y)) In other words, (g f)(x) = (g f)(y) Since g f is injective, we conclude that x= y Part (b) We did this in class We will disprove the statement by providing a counterexample Fix A = fag, B = fb 1;b 2g, C = fcg, f = f(a;b 1)g, and g = f(b.
The integrand is the product of two function x and sin (x) and we try to use integration by parts in rule 6 as follows Let f(x) = x , g'(x) = sin(x) and therefore g(x) = cos(x) Hence ∫ x sin (x) dx = ∫ f(x) g'(x) dx = ( f(x) g(x) ∫ f'(x) g(x) dx) Substitute f(x), f'(x), g(x) and g'(x) by x , 1, sin(x) and cos(x) respectively. C < 0 moves it down We can move it left or right by adding a constant to the xvalue g(x) = (xC) 2 Adding C moves the function to the left (the negative direction) Why?. G What is the expectation value of H , ie the average energy of the system, for the wavefunction Ψ given in part f?.
Aug 01, 12 · txt 1802 hdrsgml 1802 accession number conformed submission type 8k public document count 25 conformed period of report 1801 item information results of operations and financial condition item information regulation fd disclosure item. R epi f = f x;t) 2 R n 1 j x 2 dom f;. 2 Show that for a system in a nonstationary state, 7 cn φn , where c n.
S t c n b x e x a a ~ a a a d a g i a p b l x b s d t c n Œn ɂ₳ ` b. Page 1 of Chapter 2 CHAPTER 2 RING FUNDAMENTALS 21 Basic Definitions and Properties 211 Definitions and Comments A ringRis an abelian group with a multiplication operation (a,b) → abthat is associative and satisfies the distributive laws a(bc)=abacand (a b)c= ab acfor all a,b,c∈ RWe will always assume that Rhas at least two elements,including a multiplicative identity 1. F (x) g sublevel sets of convex functions are convex (converse is fa lse) epigraph of f R n!.
Therefore, the function g (x) g(x) g (x) exists and is equal to the derivative of f (x) f(x) f (x) for all x ∈ (− ϵ, ϵ) x \in (\epsilon, \, \epsilon) x ∈ (− ϵ, ϵ) It follows from induction that the n th n^\text{th} n th derivative of the power series converges in ( − ϵ , ϵ ) (\epsilon, \, \epsilon) ( − ϵ , ϵ ) and is.

Quotient Rule Wikipedia

Proof Of Taylor S Theorem Mathematics Stack Exchange
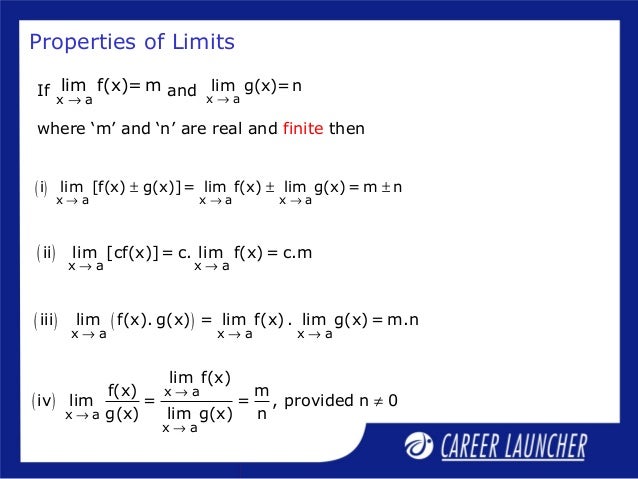
Functions Limits And Continuity
Fxg G Cn のギャラリー

Section 6 2 Calculating Coefficients Of Generating Functions
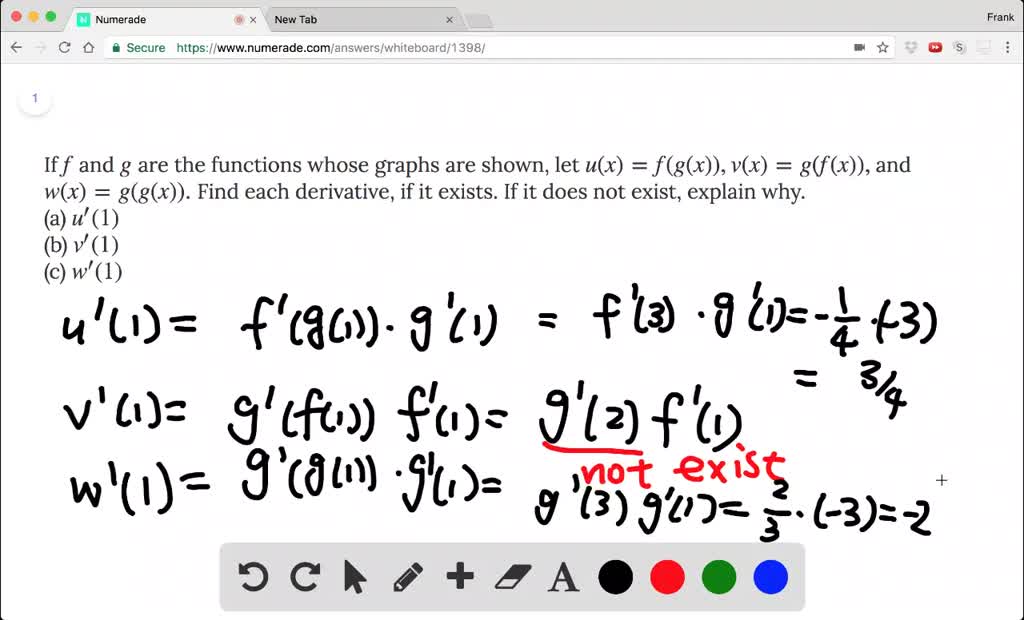
Solved If F And G Are The Functions Whose Graphs
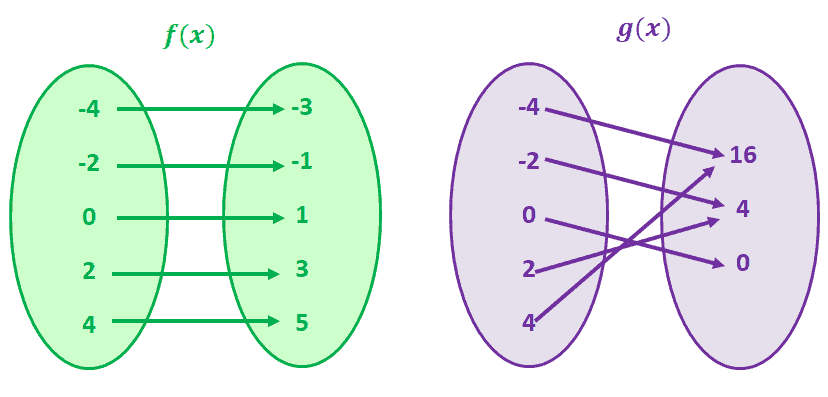
One To One Function Explanation Examples

Solved Let C Be A Constant Then If F X C Its Derivati Chegg Com

Section 6 2 Calculating Coefficients Of Generating Functions

Solved Find Each Of The Following Functions F X 1 G X Chegg Com

If Y Determinant F X G X H X L M N A B C Prove Dy Dx F X
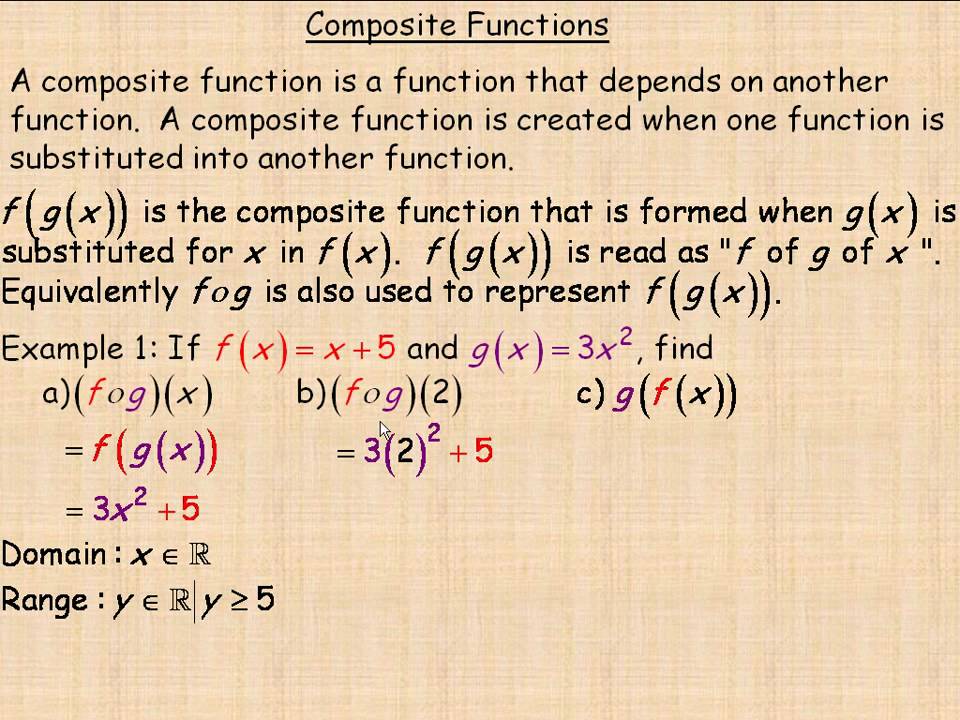
Composite Functions Video Lessons Examples And Solutions

Solved 4 Pair Functions Determine Whether F X O G X Whether G Z O F Z One Function Big O Give Va Q
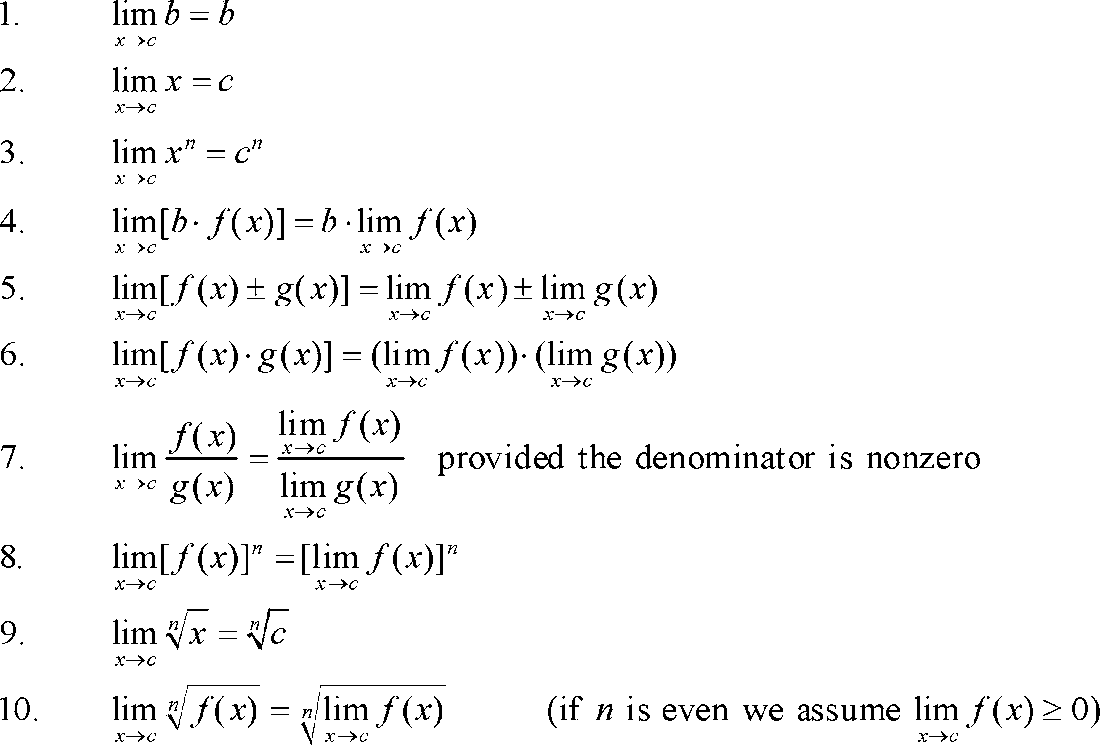
Calculus Learning With Ms Lin

Solved Find Each Of The Following Functions F X X 5 Chegg Com

Consider The Functions F X And G X Both Defined From R R
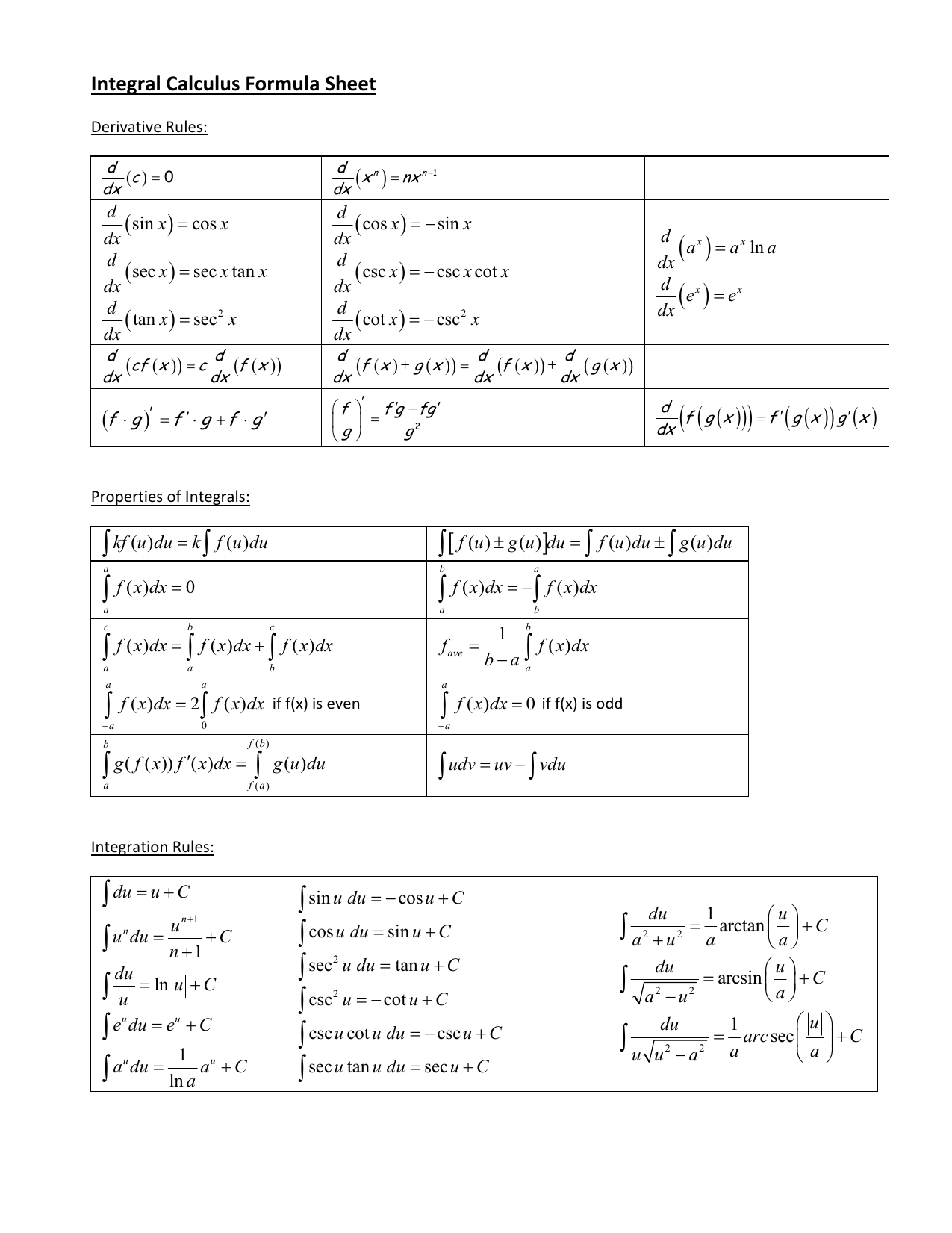
Integral Calculus Formula Sheet 0

Reading The Definite Integral Applied To Area Business Calculus

Consider The Functions F X And G X Both Defined From R R
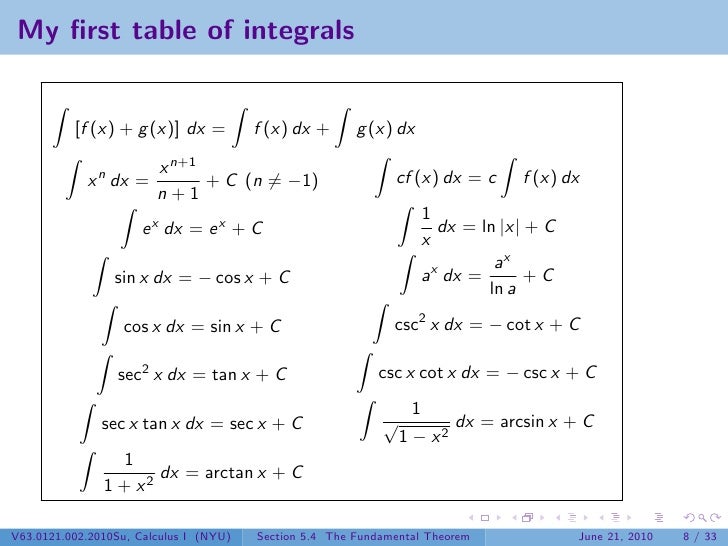
Lesson 27 The Fundamental Theorem Of Calculus

An Introduction To Partial Differential Equation With Matlab Pages 101 150 Flip Pdf Download Fliphtml5

Limits Tutorial

If G X 2h X H X 2h X H X Where H X Sinx Sin N X
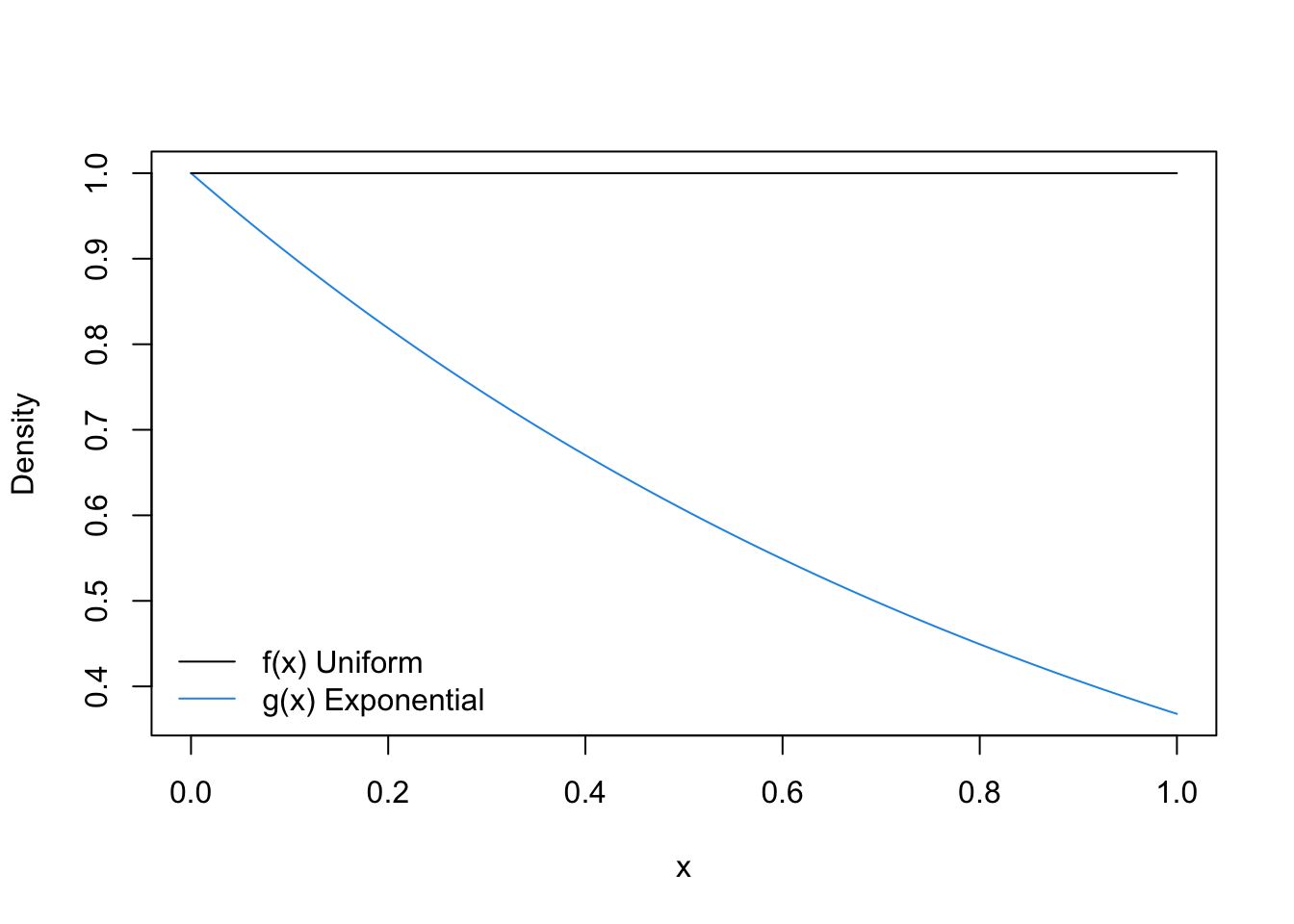
6 3 Rejection Sampling Advanced Statistical Computing

Function Definition Types Examples Facts Britannica

Additional Mathematics Functions Questions 1 Given Function F X Mx 4 X N X N If F 2 10 And F 8 4 Find A The Values Of M And N B The Ppt Download

Portmanteau Theorem And Central Limit Theorem
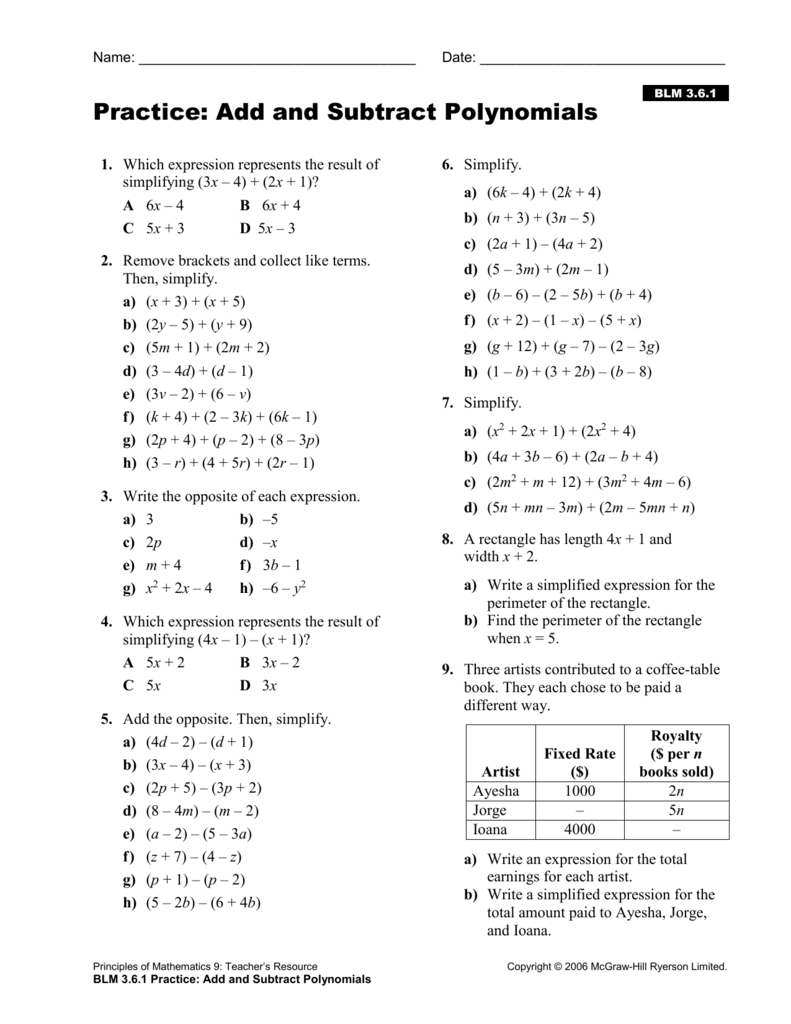
Add And Subtract Polynomials Practice

Answered D Y 0 140 If Y X 1 X 2 X Bartleby

Ibc Ched Basic Calculus Formula Maxima And Minima Integral

Let F X G X X W H E Nx 0 And F 0 0 If G 0 G Prime

If F X And G X Are Quadratic Functions But F G X Produces The Graph Below Which Statement Must Brainly Com
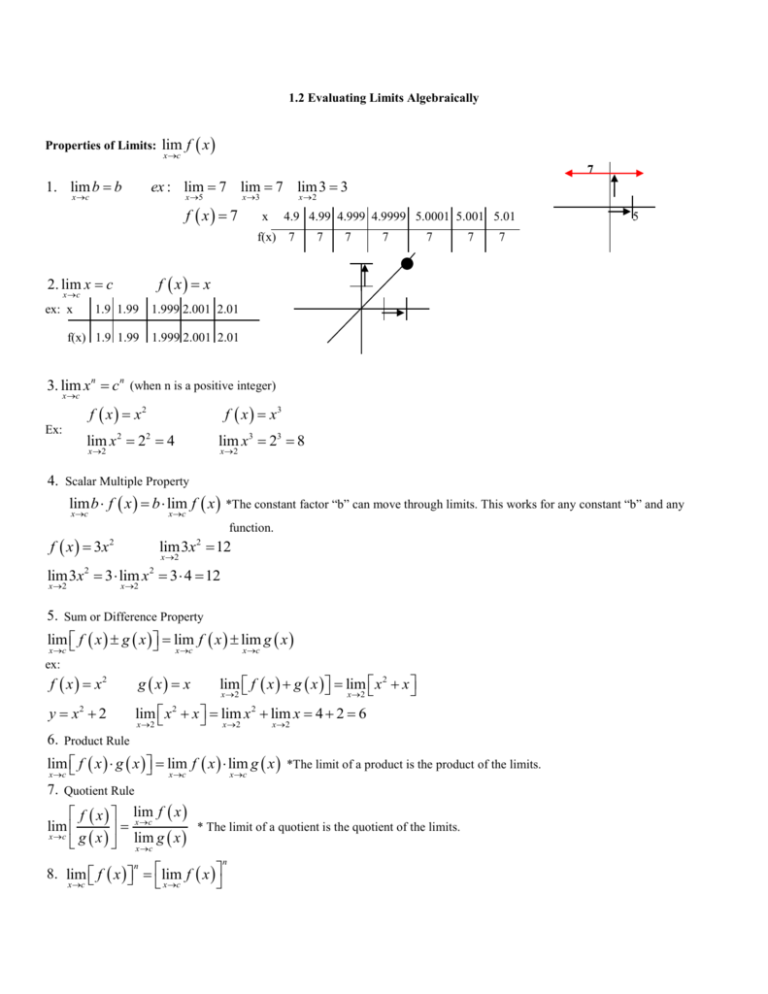
1 2 Notes Evaluating Limits Algebraically
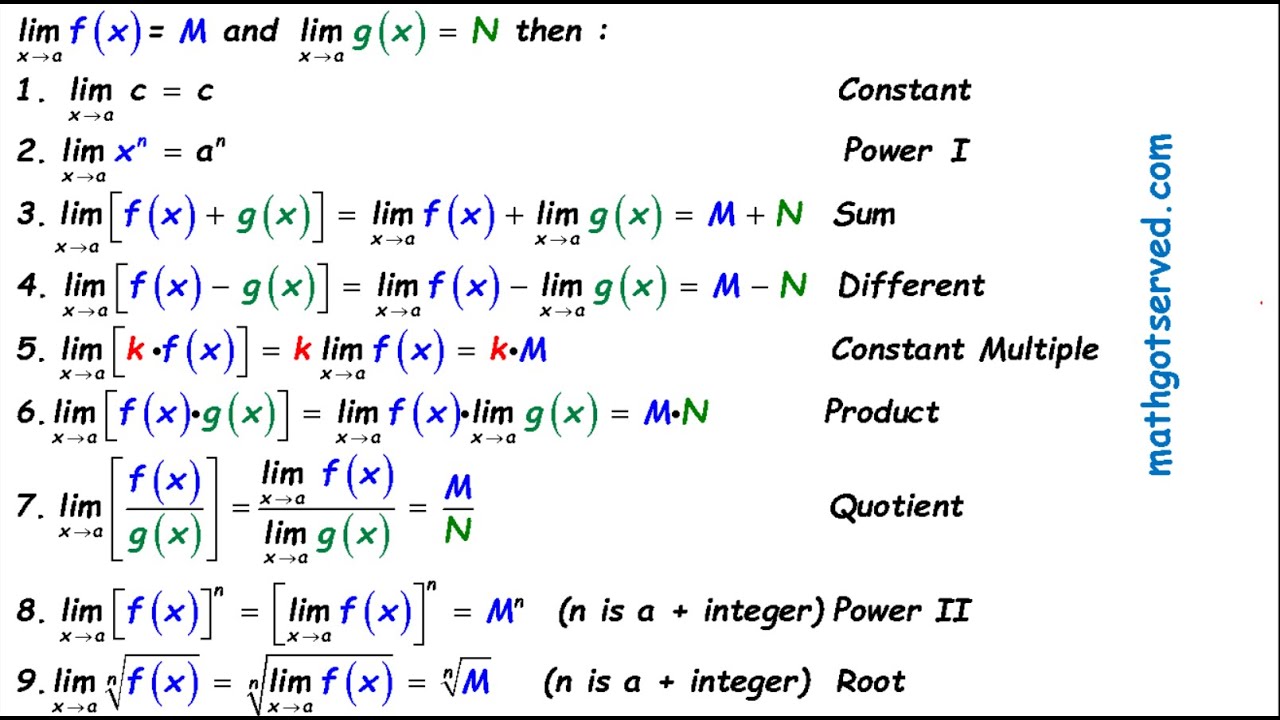
Limit Laws To Evaluate Understand Limits Ap Calculus Ab Exam Mathgotserved Lim Lecture Using Calc Youtube

Introduction To Antiderivatives
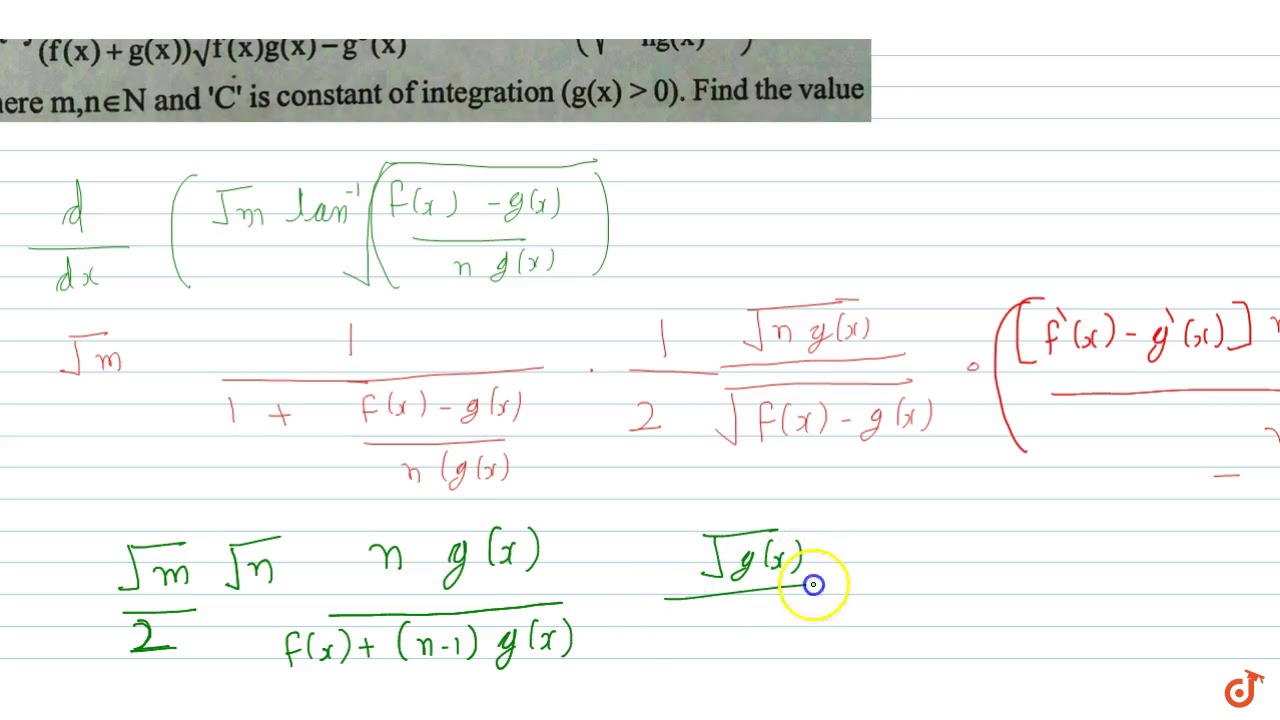
If Int F Prime X G X G Prime X F X F X G X Sqrt F X G X G 2 X D X Sqrt M Tan Youtube
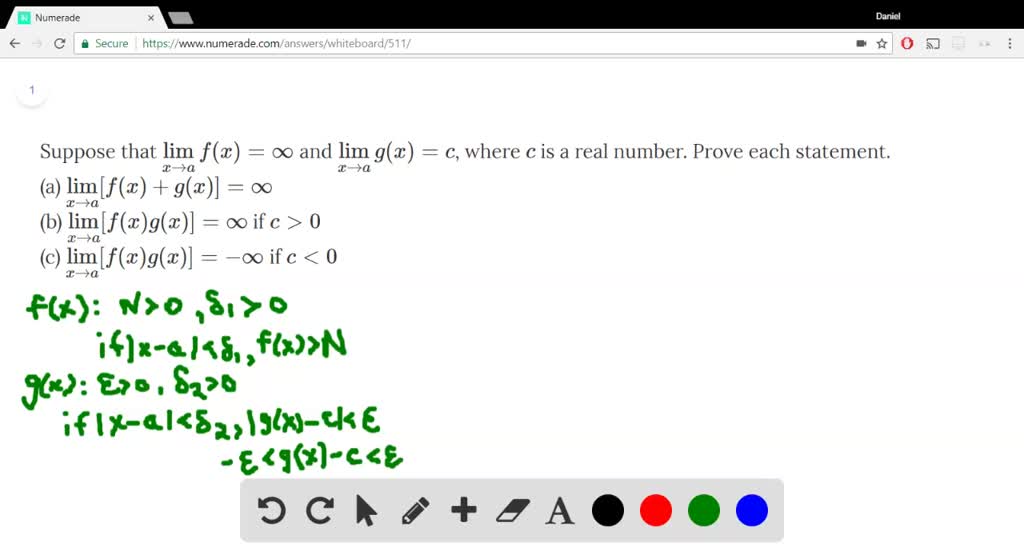
Solved Suppose That Displaystyle Lim X To A
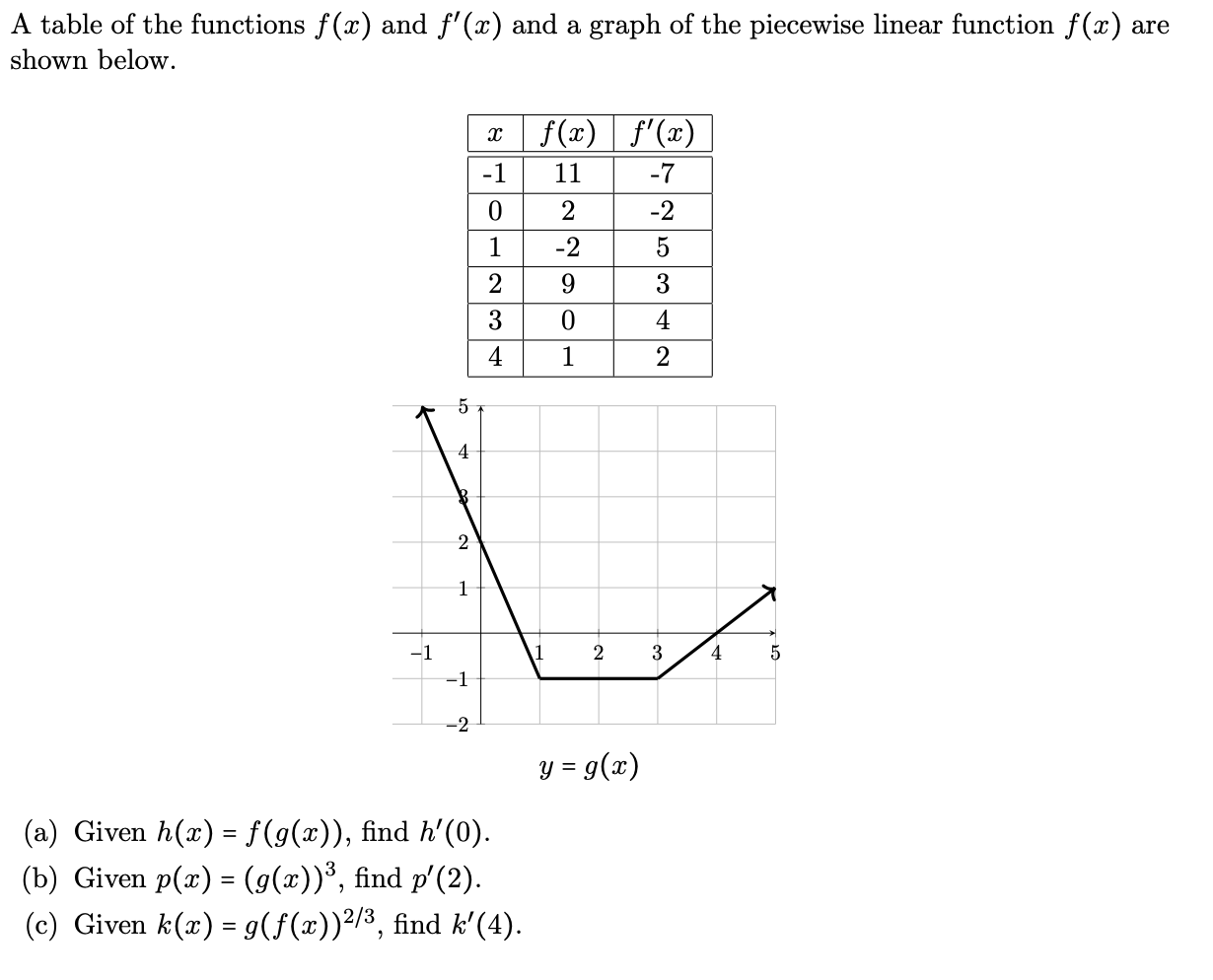
Solved A Table Of The Functions F X And F X And A Grap Chegg Com
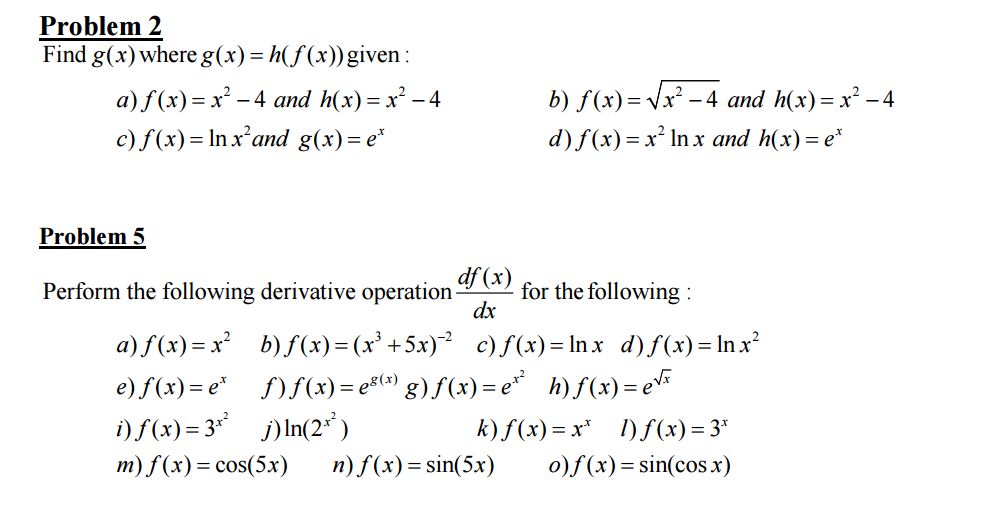
Solved Find G X Where G X H F X Given F X X 2 Chegg Com
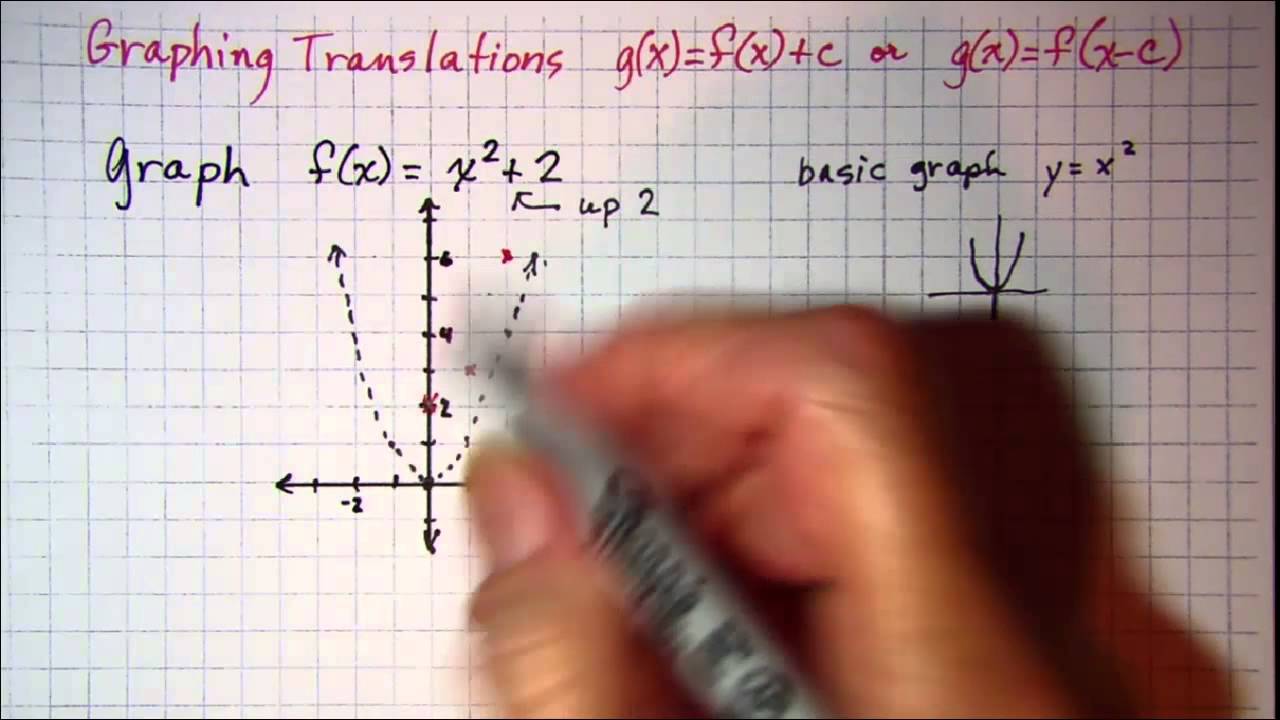
Graphing Translations G X F X C Or G X F X C Youtube

Solved Problem 4 Let F G Be Functions Which Are Both Dif Chegg Com

Let F X Be A N Degree Polynomial Function Having N Real And Distinct Roots If G X F X 100f X Mathematics Stack Exchange

Let F X X2 2x 15 And G X X3 See How To Solve It At Qanda

Consider The Table For F X And The Graph For G X Which Statement Is True When Comparing The Brainly Com

Given F X And G X K F X Use The Graph To Determine The Value Of K A 3 B 1 3 C 1 3 D Brainly Com

Ap Calculus Chapter 1 Section 3 Ppt Video Online Download

Composing Functions Article Khan Academy
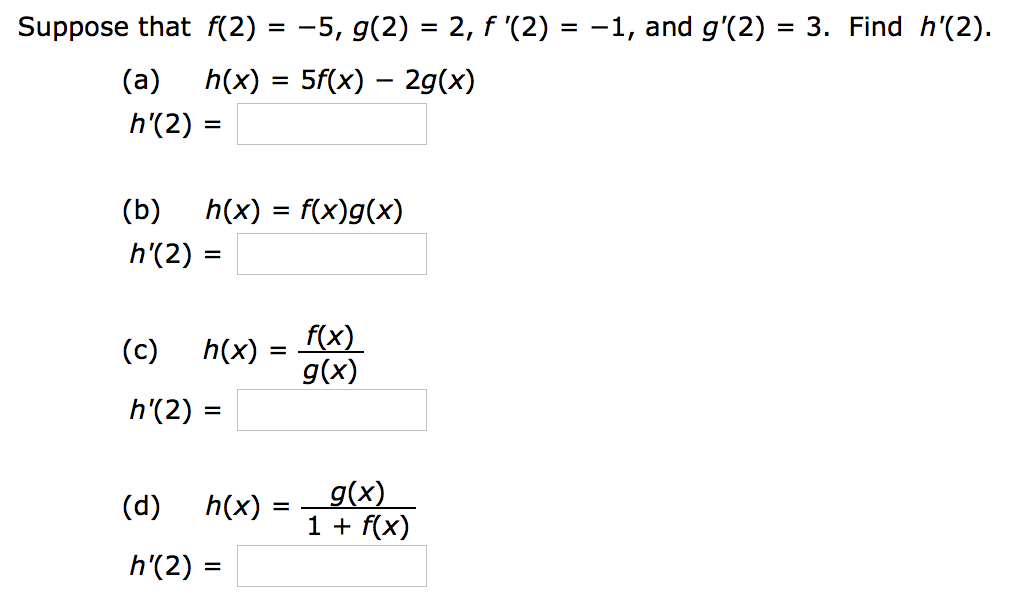
Solved Suppose That 2 5 G 2 2 F 2 1 And G 2 3 Chegg Com

If F X Is A Differentiable Function And G X Is A Double Differentiable Function Such That F X 1 And F X G X If F 2 0 G 2 0 9 Such That There Exists

Show That Parseval S Theorem For Two Real Functions Whose Fourier Expansions Have Cosine And Sine Coefficients An Bn And An Bn Takes The Form 1 L 0 L F X G

Suppose Fa N Dg Are Functions Having Second Derivative F A

Low Degree Testing In Zk Stark Part 1 By Kitten Finance Apr 21 Medium

Calculus Basics 微积分基础 Issue 49 Solomonxie Solomonxie Github Io Github

Suppose Fa N Dg Are Functions Having Second Derivative F A

Integrals Cheat Sheet Pauls Online Math Notes

1 Vytah

Direct Substitution Find Limits In Easy Steps Calculus How To

Ax B And G X Cx

How To Simplify This Composition Function G X Underset N Text Times Underbrace F Circ F Circ F Circ F Circ F Circ Cdots Circ F X Mathematics Stack Exchange

Section 6 2 Calculating Coefficients Of Generating Functions

Answered 7 7 Consider Two Functions F And G On Bartleby
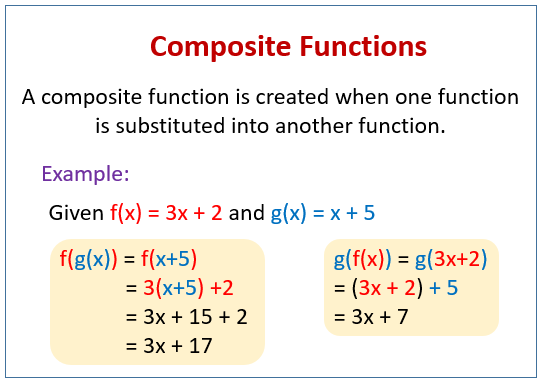
Composite Functions Video Lessons Examples And Solutions

Solved 1 Use The Table Below To Find The Following Deriv Chegg Com
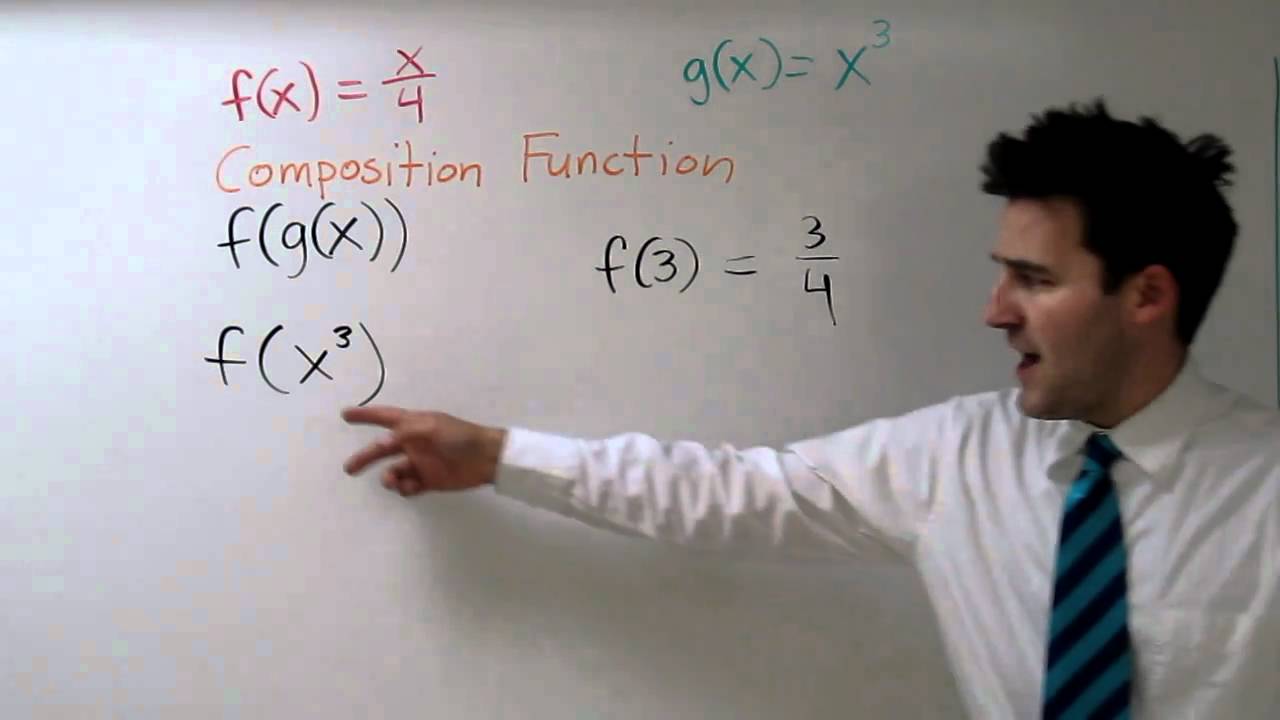
Composite Functions F G X And G F X Youtube

The Following Are Notations F See How To Solve It At Qanda

The Geometry Of The Generalized Inverse G Of A Linear Mapping F Here X Download Scientific Diagram

Answered Assume F G Are Differentiable Bartleby

Math 1304 Calculus I 3 2 The Product And Quotient Rules Ppt Download

Exactly five R A B But Not Uniformly Flip Ebook Pages 1 5 Anyflip Anyflip

Solved The Chain Rule For Differentiation Is F Composite Chegg Com

Function Mathematics Wikipedia
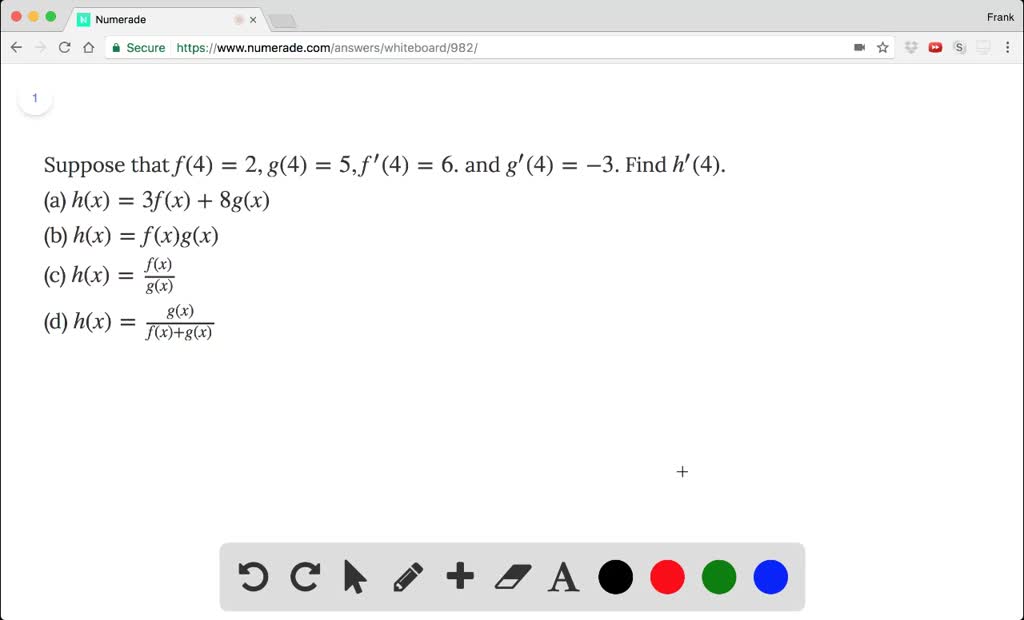
Solved Suppose That F 4 2 G 4 5 F 4 6
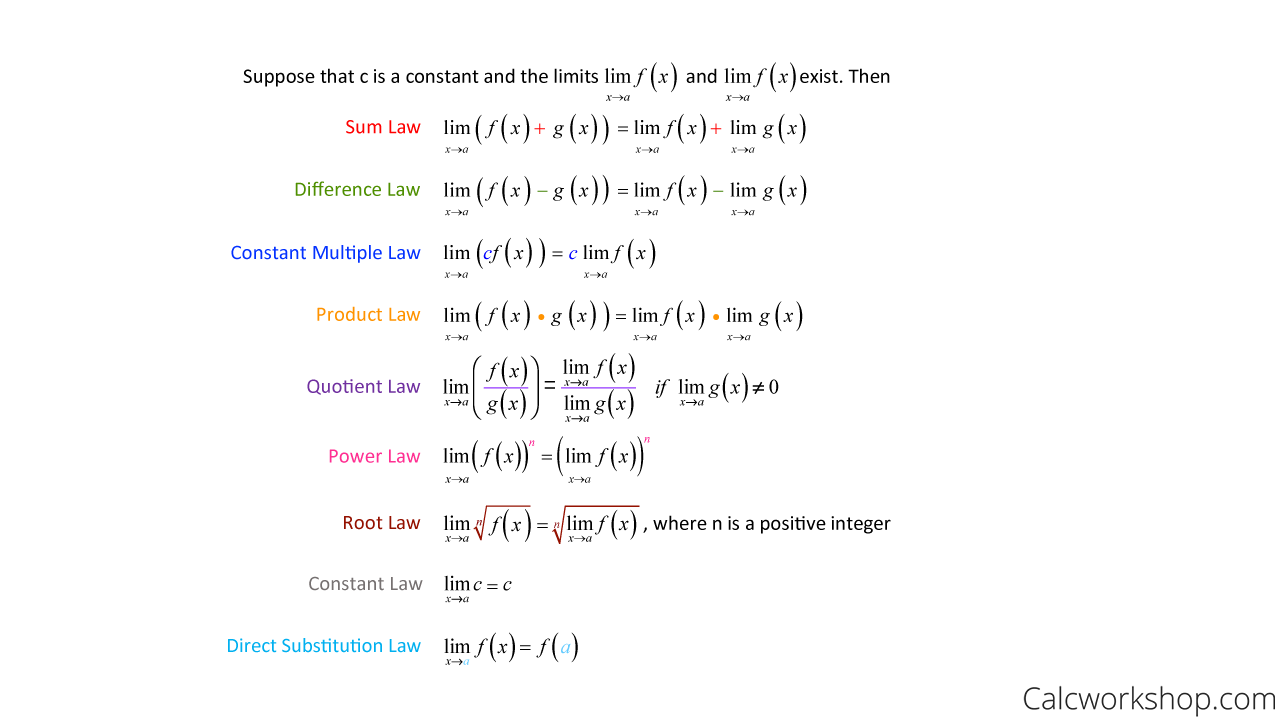
Limit Rules Explained W 5 Step By Step Examples

Limits Calculus Study Guide
Composition Of Functions Composing Functions At Points

Inverse Function Wikipedia
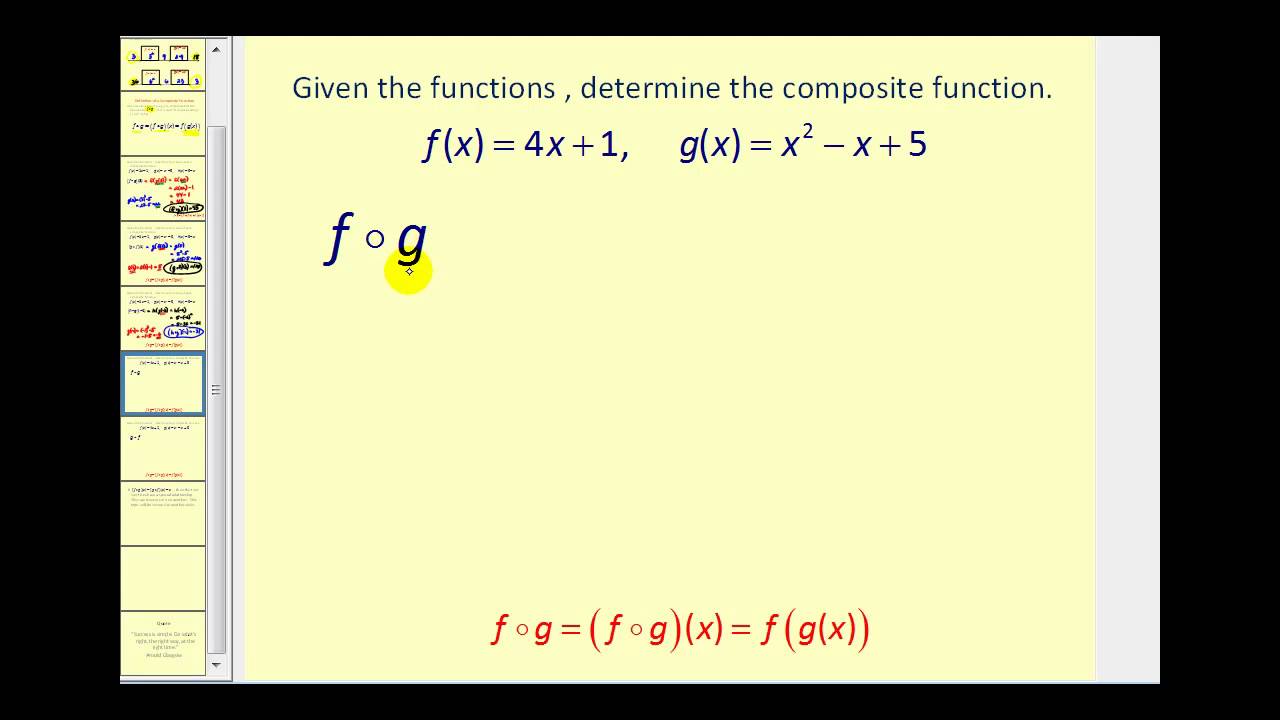
Composite Functions Video Lessons Examples And Solutions

Additional Mathematics Functions Questions 1 Given Function F X Mx 4 X N X N If F 2 10 And F 8 4 Find A The Values Of M And N B The Ppt Download

Integration
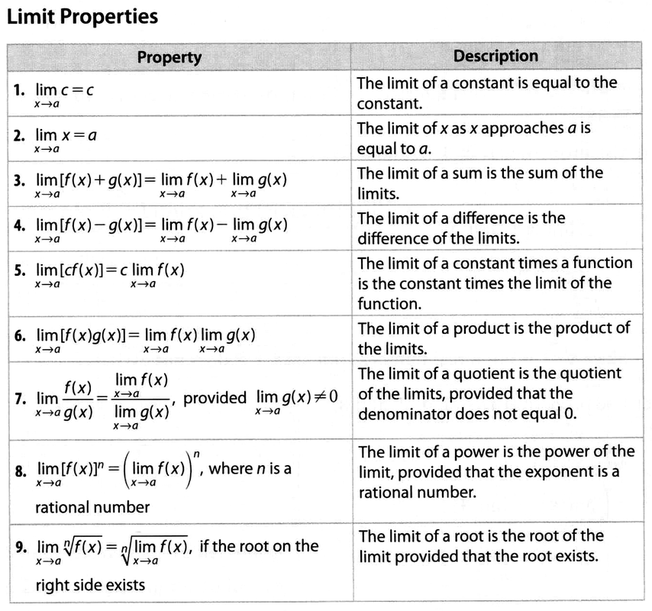
Section 1 4 Ghci Grade 12 Calculus Vectors




