Cn Fxg G
F(a) andf(b) Thenthere is a number c in a,b such thatf(c) = N 3A preliminary result about the definite integral Theorem Let f(x) be a continuous function on the interval a,b Then there exists a c in a,b forwhich f(c) (b a) = ∫ b a f(x)dx This theorem essentially says that if you take the area under f(x) over the interval a,b.
Cn fxg g. Feb 19, · In this section we discuss how the formula for a convergent Geometric Series can be used to represent some functions as power series To use the Geometric Series formula, the function must be able to be put into a specific form, which is often impossible However, use of this formula does quickly illustrate how functions can be represented as a power series. N=0 c n4 n is convergent, does it follow that the following series are convergent?. Solve your math problems using our free math solver with stepbystep solutions Our math solver supports basic math, prealgebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and more.
T @ ~ R s ^ w _ ̓` x ̊e _ W O U B } b v A C e A X ^ AGBA Łw _ ̓` x ɂ Ή S U B Ƀ\ t g r e f ȂǁB. #title #points 687 #rows 1097 #sense 1 #xorigin 739 #yorigin #rotation 0 #ptseparation 005 #rwseparation 005 #transform #unit_length km,1000 #map_projection "nad27 / *lcc90" nad27,,,0. The answer is that it depends on what kinds of statements are used.
F X g ^ Ȃ犔 Ѓt @ C N t @ C N ł́A i Ə ҂Ƃ̏o ̐ړ_ ł u X v ɖڂ A i ŏ ҂̍w s N ׂ̂ ` Ēv ܂ B. D q } j t F X g x ́A } j t F X g d q āA r o ƎҁA W ^ ƎҁA Ǝ҂ 3 ҂ Z ^ l b g N ł 肷 d g ݂ł B @ 13 2 ̋K Ɋ Â A i j { Y Ɣp U Z ^ S 1 ́u Z ^ v Ƃ Ďw 肳 A d q } j t F X g ̉^ c s Ă ܂ B d q } j t F X g 𗘗p ꍇ ɂ́A r o Ǝ҂ƈϑ ̎ W ^ ƎҁA Ǝ҂ 3 ҂̉ K v ł A d q ̃ b g ł u ̋ L v Ɓu ` B ̌ v ɂ A W ҊԂ. 1c C n 1c n 1 C nc n = P0(c) = P(1) P(0) 1 0 = 0 This completes the proof 55Suppose fis de ned and di erentiable for every x>0, and f0(x) !0 as x!1 Put g(x) = f(x 1) f(x) Prove that g(x) !0 as x!1 Rudin’s Ex 5 Proof Let >0 be given Since f0(x) !0 as x!1, there exists Nsuch that x Nimplies jf0(x)j< Thus, for x N, by the Mean.
For example, f gis measurable provided that f(x), g(x) are not simultaneously equal to 1and 1 , and fgis is measurable provided that f(x), g(x) are not simultaneously equal to 0 and 1 Proposition 37 If f;g X!R are extended realvalued measurable functions, then c n ˜ E n (x) where c 1. Equações f(x) = g(x) Discutir a quantidade de soluções reais de uma equação `g(x) = f(x)` pode ser facilitada pela exibição no mesmo plano cartesiano dos gráficos de `g(x)` e `f(x)` Dispensando o uso de calculadoras e/ou programas CAM (computer aided mathematics) um bom esboço dos gráficos de f e g vai ajudar a análise da equação. R We say that f(n) 2 ( g(n)) (read f is BigTheta of g) if there exist constants c1;c2 2 R and n0 2 N such that for every integer n n0, c1g(n) f(n) c2g(n) I Intuition f is (asymptotically ) equal to g I f is bounded above and below by g I BigTheta gives an asymptotic equivalence.
(a) X∞ n=0 c n(−2)n Yes If P ∞ n=0 c n4 n is convergent, then the radius of convergence for the power series P ∞ n=0 c nx n is at least 4 Therefore the interval of convergence contains 2 (b) X∞ n=0 c n(−4)n No Consider the power series X∞ n=0. Big O notation is a mathematical notation that describes the limiting behavior of a function when the argument tends towards a particular value or infinity Big O is a member of a family of notations invented by Paul Bachmann, Edmund Landau, and others, collectively called Bachmann–Landau notation or asymptotic notation In computer science, big O notation is used to classify. Assume g fis injective We need to show fis injective So let x;y2nd assume f(x) = f(y) Applying gto both sides yields g(f(x)) = g(f(y)) In other words, (g f)(x) = (g f)(y) Since g f is injective, we conclude that x= y Part (b) We did this in class We will disprove the statement by providing a counterexample Fix A = fag, B = fb 1;b.
Free math lessons and math homework help from basic math to algebra, geometry and beyond Students, teachers, parents, and everyone can find solutions to their math problems instantly. X g A t @ ~ R s ^ f B X N V X e ŁiFDS j A тɃt @ ~ R s ^ ŁiFC j A. About HomeSnacks HomeSnacks is based in Raleigh, NC We aim to deliver bitesized pieces of infotainment about where you live We use data, analytics, and a sense of humor to determine quality of life for places across the nation.
F(x) g(x) It makes sense, then, to consider the function f to be the function g Conditions for Ordering RealValued Functions For functions f and g de ned on the same domain and taking values in R, we have f g if and only if f(x) g(x) for all x in their common domain (F2) The same conditions apply with >,. Then inf F g(x) f(x) g(x) supff(x) g(x) jx2Xg Similarly, let f(x)supG2ff(x)supGjx2Xgand g(x) 2G Then, f(x)supG f(x) g(x) infff(x) g(x) jx2Xg Hence, inf H inf F inf G supHwhich proves inequalities8and9 We now give examples to show that each inequality can be strict Let X= fx2R j 1 x 1g= 1;1 and consider functions f X!R, g. E C N X v f X ͉f ̃v t F b V i ł Ɨp r f I A L f A e C x g L ^ f Ȃǂ̊ E A DVD, u C f B X N A web p t @ C ̐ ܂ŁA.
BigTheta De nition De nition Let f and g be two functions f;g N !. The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus, Part 1 If f is continuous on a,b, then the function g defined by g(x) = Z x a f(t)dt a ≤ x ≤ b is continuous on a,b and differentiable on. Lftnf(t)g= ( 1)n dn dsn F(s) (21) Thus, Lftsin2tg= 4s (s2 4)2 15 Let F(s) = Lff(t)g Then Lff0(t)g= f(0) sF(s);.
Problem Set 5 Solutions Sam Elder October 15, 15 Problem 1 (3111) Let fbe a polynomial of degree n, say f(x) = P n k=0 c kx k, such that the rst and last coe cients c 0 and c n have opposite signs Prove that f(x) = 0 for at least one positive x. In general, 1to1 of f and g does not always imply 1to1 of f g 12 Properties of OneToOne Functions Properties Properties If f and g are onetoone, then f g is onetoone Proof f g(x 1) = f g(x 2) ⇒ f(g(x 1)) = f(g(x 2)) ⇒ g(x 1) = g(x 2) ⇒ x 1 = x 2 Examples 4 • f(x) = 3x3 − 5 is onetoone, since f = g u where g(u) =. That fgis di erentiable at every point x2Uand that its derivative is equal to f(x)g0(x)g(x)f0(x) = fDg gDf Note that this derivative is unique by Theorem 912 in Rudin 3 Let T be a linear transformation from Rn to R m Show that T Rn!R is di erentiable as a map.
Stack Exchange network consists of 176 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow, the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers Visit Stack Exchange. Derivative examples Example #1 f (x) = x 3 5x 2 x8 f ' (x) = 3x 2 2⋅5x10 = 3x 2 10x1 Example #2 f (x) = sin(3x 2) When applying the chain rule f ' (x) = cos(3x 2) ⋅ 3x 2' = cos(3x 2) ⋅ 6x Second derivative test When the first derivative of a function is zero at point x 0 f '(x 0) = 0 Then the second derivative at point x 0, f''(x 0), can indicate the type of that point. G ( N = rN 1 N K to N that K and r constantsedu/~ma137 18 6/12 Di erentiation Rules Examples ofs 4 150) to f ( x = cx3 2 at x = that c constantedu/~ma137 18 7/12 Di erentiation Rules Examples ofs 5 graph of f ( x at x Using estimate that f = f 0 = the of g ( x 5 x f ( x ) x y 2 f ( x ) at x rm y = mx b where m = b = edu/~ma137 18 8.
Feb 23, 21 · all real numbers x, y, and z Prove that there exists a function g R !R such that f(x;y) = g(x) g(y) for all real numbers xand y 26 08 Alan and Barbara play a game in which they take turns lling entries of an initially empty 08 08 array Alan plays rst At each turn, a player chooses a real number and places it in a vacant entry. G for all x2X Therefore, i f i g f(x) g(x) s f i f all x2X So i f i g 2R is a lower bound of ff(x) g(x) x2Xg and s f s g 2R is an upper bound of ff(x) g(x) x2Xg So we have the two desired inequalities Let f(x) = 0 for every x2Xbe the zero function and gbe any bounded function. V ・・・E ・・03 N9 ・/title> r { h ・ ・ \ V ・・・E ・・ \ r.
Equivalent to limx f(x)/g(x) = 0 Also, if a is some real number, we write f(x) = o(g(x)) (3 * N2 5) > (c * N) ˘ ˇ ˆ In general, how can you determine the running time of a piece of code?. 3240 W 71 st Ave, Unit 5 Westminster CO (Address of Principal Executive Offices, Zip Code) (7) (Registrant's Telephone Number, Including Area Code). Find (f g)(x) for f and g below f(x) = 3x 4 (6) g(x) = x2 1 x (7) When composing functions we always read from right to left So, rst, we will plug x into g (which is already done) and then g into f What this means, is that wherever we see an x in f we will plug in g That is, g acts as our new variable and we have f(g(x)) 1.
Jun 12, 14 · f(x)g(x)f(x)−g(x) f (x)⋅g(x) f(x) g(x) g(x) ≠ 0 Many of the problems we will work in this lesson are problems you may already know how to do You will just need to get used to some new notation We will start with the operations of addition and subtraction Problem 1 WORKED EXAMPLE – Adding and Subtracting Functions. Select all that apply Of(x) = (g(x)) For every n that is large enough f(n)'s 100g(n) gx) E {h(x) 35c>n2s (h(n) sc f(n)) } gix) Off(x)) For every n that is large enough gin) s 100f(n) f(x) = {h(x) 3s, conshin) sc g(n))} Given any two nondecreasing functions f(x) and g(x. (Leting g(x) = xn yields moments for example) Finally, the variance of X is denoted by Var(X), defined by E{X − E(X)2}, and can be computed via Var(X) = E(X2)−E2(X), (2) the second moment minus the square of the first moment We usually denote the variance by σ2 = Var(X) and when necessary (to avoid confusion) include X as a subscript.
View FormulaSheetConcisepdf from MATH 119A at University Of Arizona Parameters c, n, and k are constants,and f (X) and g(X) are differentiable functions Constant (c)0 = 0 Power (X n )0 = nX. De ne g(x) = P n 1 k=0 c k1x k This is clearly a polynomial, so it remains to show it is degree n 1 Since f is degree n 1, c n 6= 0 But c n is also the coe cient on the highestdegree term, xn 1, in g(x), so g(x) is degree n 1, as desired Part 52 For each real a, the function p given by p(x) = f(x a) is a polynomial of degree n Solution. Given any two nondecreasing functions fx) and g(x) such that f(x) = O(g(x)), which of the following are always true?.
(22) and Lff00(t)g= sf(0) f0(0) s2F(s) (23) 16 The convolution of functions f(t) and g(t) is (f g)(t) = Z t 0 f(t u)g(u)du (24) As we showed in class, convolution is commutative, ie (f g)(t) = Z t 0 f(t u)g(u)du= Z t 0 f. S t c n b x e x a a ~ a a a d a g i a p b l x b s d t c n Œn ɂ₳ ` b. Dec 10, · 8 Consider the functions f(x), g(x), h(x) as given below Show that (fog)oh = fo(goh) in each case (i) f(x) = x – 1, g(x) = 3x 1 and h(x) = x^2.
Mar 01, 18 · h'(1)=16/3 The product rule states, if h(x)=f(x)g(x), then h'(x)=f'(x)g(x)f(x)g'(x) We are ask to find h'(1), or by the product rule h'(1)=f'(1)g(1)f(1)g'(1) The values of the functions must be f(1)=2 and g(1)=4/3 Remember the derivative gives the slope of any given point, but as we can see in the figures these must correspond, to the slope of the line, which. More formally, f = g if f(x) = g(x) for all x ∈ X, where fX → Y and gX → Y 8 9 note 4 The domain and codomain are not always explicitly given when a function is defined, and, without some (possibly difficult) computation, one might only know that the domain is contained in a larger set. MATH 140B HW 5 SOLUTIONS Problem1(WR Ch 7 #8) If I(x) ˘ 0 (x •0),1 (x ¨0),if {xn} is a sequence of distinct points of (a,b), and ifP jcnj converges, prove that the series f (x) ˘ X1 n˘1 cnI(x¡xn) (a •x •b) converges uniformly, and that f is continuous for every x 6˘xn Solution Let fk(x) ˘ Xk n˘1 cnI(x¡xn) By the Weierstrass Mtest (Theorem 710) with Mn ˘jcnj, {fk(x.
225 South Sixth Street Minneapolis, Minnesota (612) March 8, 02 Dear Shareholders You are cordially invited to join us for our 02 annual meeting of shareholders, which will be held on Tuesday, April 16, 02, at 1100 am, Central Time, at the America's Center, 701 Convention Plaza in downtown St Louis, Missouri. 5 2 Given the functions f(x) = x2 and g(x) = 3, sketch the graph of the combined function y = f(x) −g(x) 3 If h(x) = g(x) ÷f(x) and h(x) = x −4 2 −x, determine g(x) and f(x) 4 The revenue function for a company selling n coffee mugs can be modelled by the function R(n) = 10n, and the total cost function can be modelled by the function C(n) = 360 6n. F(g(x)) = 2*(x 3)math^2/math 7 y = 2*(x 3)math^2 /math 7 y 7 = 2*(x 3)math^2/math 7 7 (y 7)/2 = (2*(x 3)math^2/math)/2 (y 7)/2.
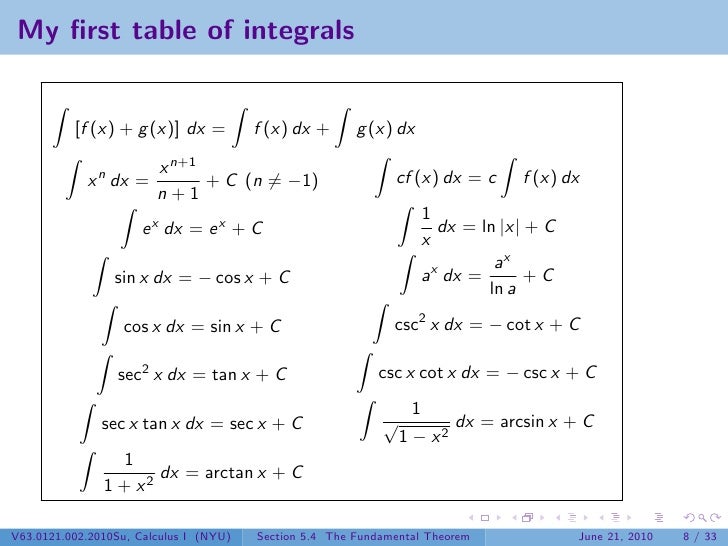
∫f(x) g(x) dx = ∫f(x) dx ∫g(x) dx Example Evaluate the integral ∫x e x dx Solution According to the above property ∫ x e x dx = ∫ x dx ∫ e x dx ò x dx is given by 13 and ∫ e x dx by 41 in table of integral formulas, hence ∫ x e x dx = x 2 / 2 e x c 4.

Section 6 2 Calculating Coefficients Of Generating Functions

Consider The Table For F X And The Graph For G X Which Statement Is True When Comparing The Brainly Com

Analiza Matematyczna I Powtorki Studocu
Cn Fxg G のギャラリー

If G Is The Inverse Of F And F X 1 1 X N Prove That G

If G X 2h X H X 2h X H X Where H X Sinx Sin N X

Integration

Section 6 2 Calculating Coefficients Of Generating Functions

Ap Calculus Chapter 1 Section 3 Ppt Video Online Download

1 Vytah

Additional Mathematics Functions Questions 1 Given Function F X Mx 4 X N X N If F 2 10 And F 8 4 Find A The Values Of M And N B The Ppt Download

Consider The Functions F X And G X Both Defined From R R

Proof Of Taylor S Theorem Mathematics Stack Exchange
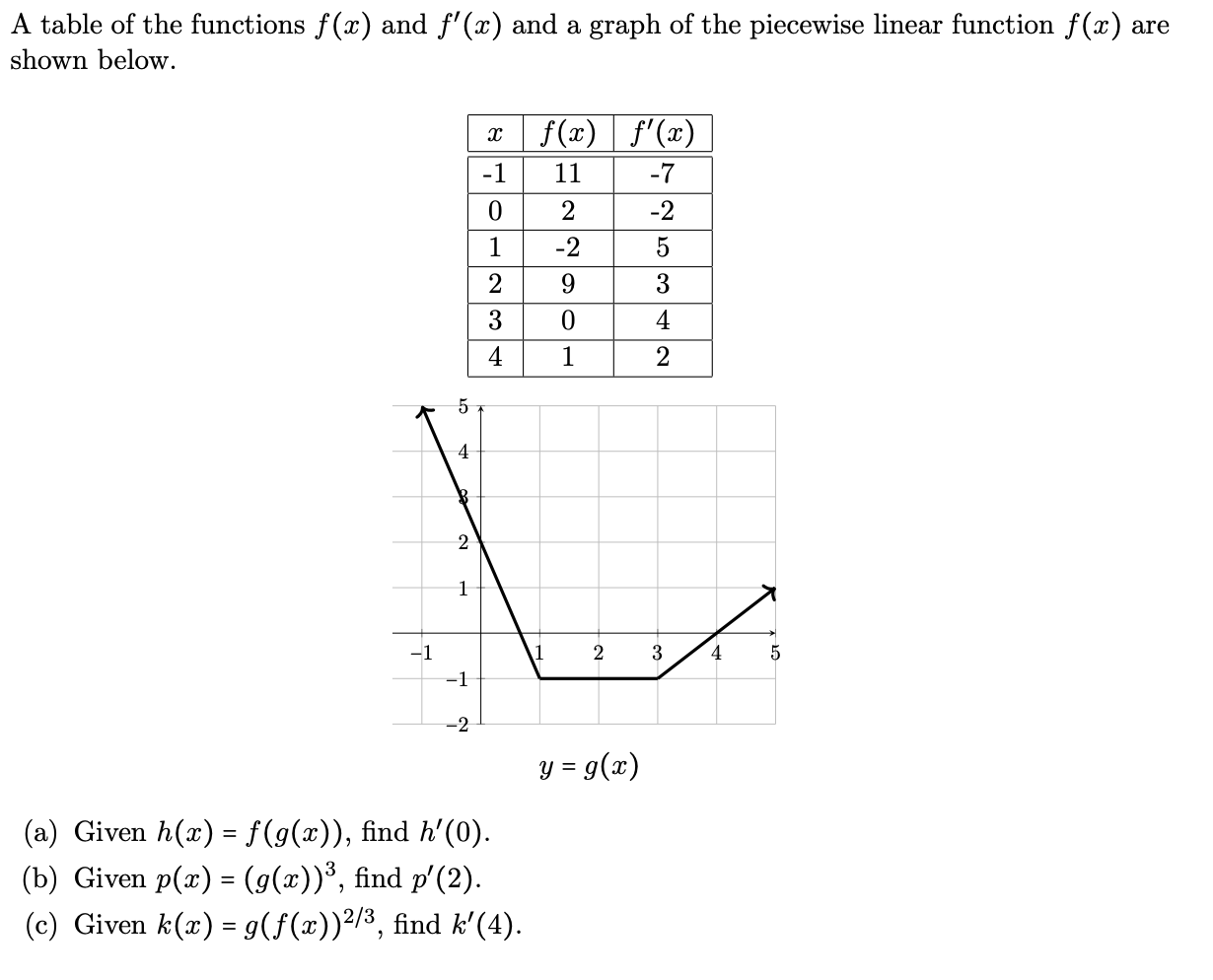
Solved A Table Of The Functions F X And F X And A Grap Chegg Com

Calculus Cheat Sheet Derivative Theoretical Physics
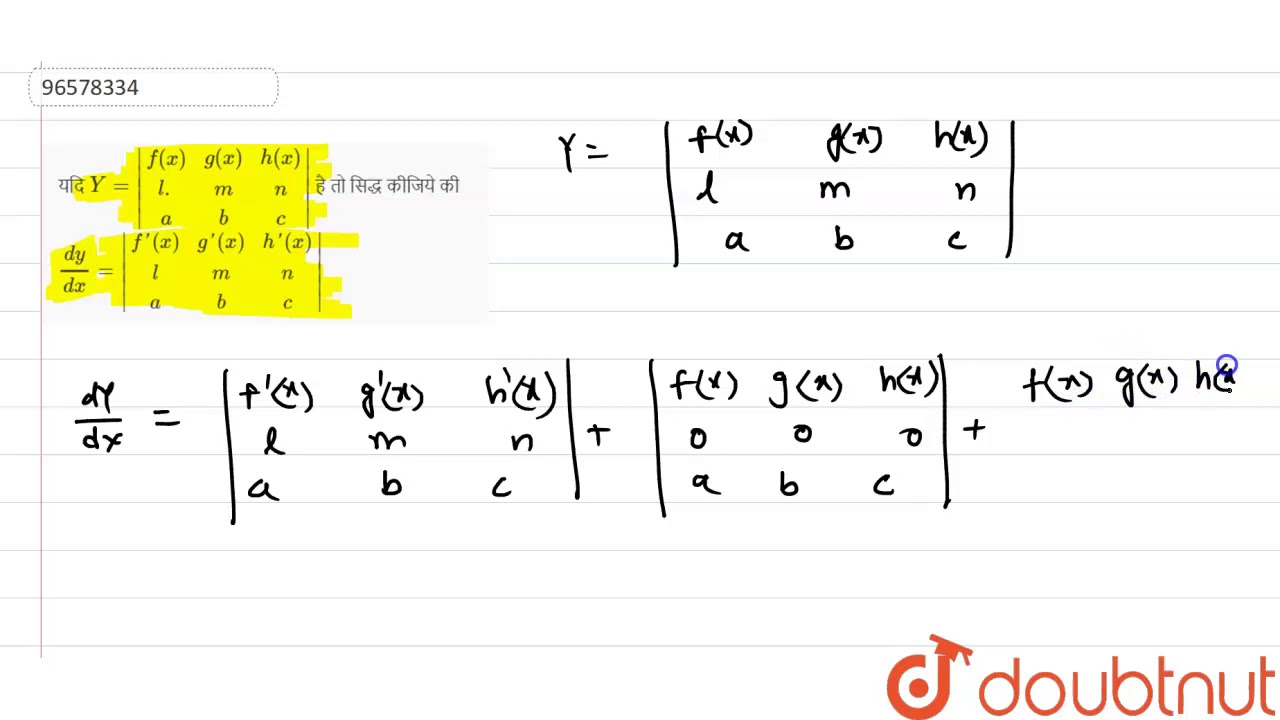
यद Y F X G X H X L M N A B C ह त स द ध क ज य क Dy Dx F X G X H Youtube

Godox Xpro Xpro C N O S F P 2 4g Ttl Flash Bezprzewodowy Wyzwalacz Nadajnika X System Hss 1 8000s Dla Canon Nikon Sony Olympus Fuji Przycisk Wyzwalania Migawki Aliexpress
Functions Limits And Continuity

Consider The Functions F X And G X Both Defined From R R
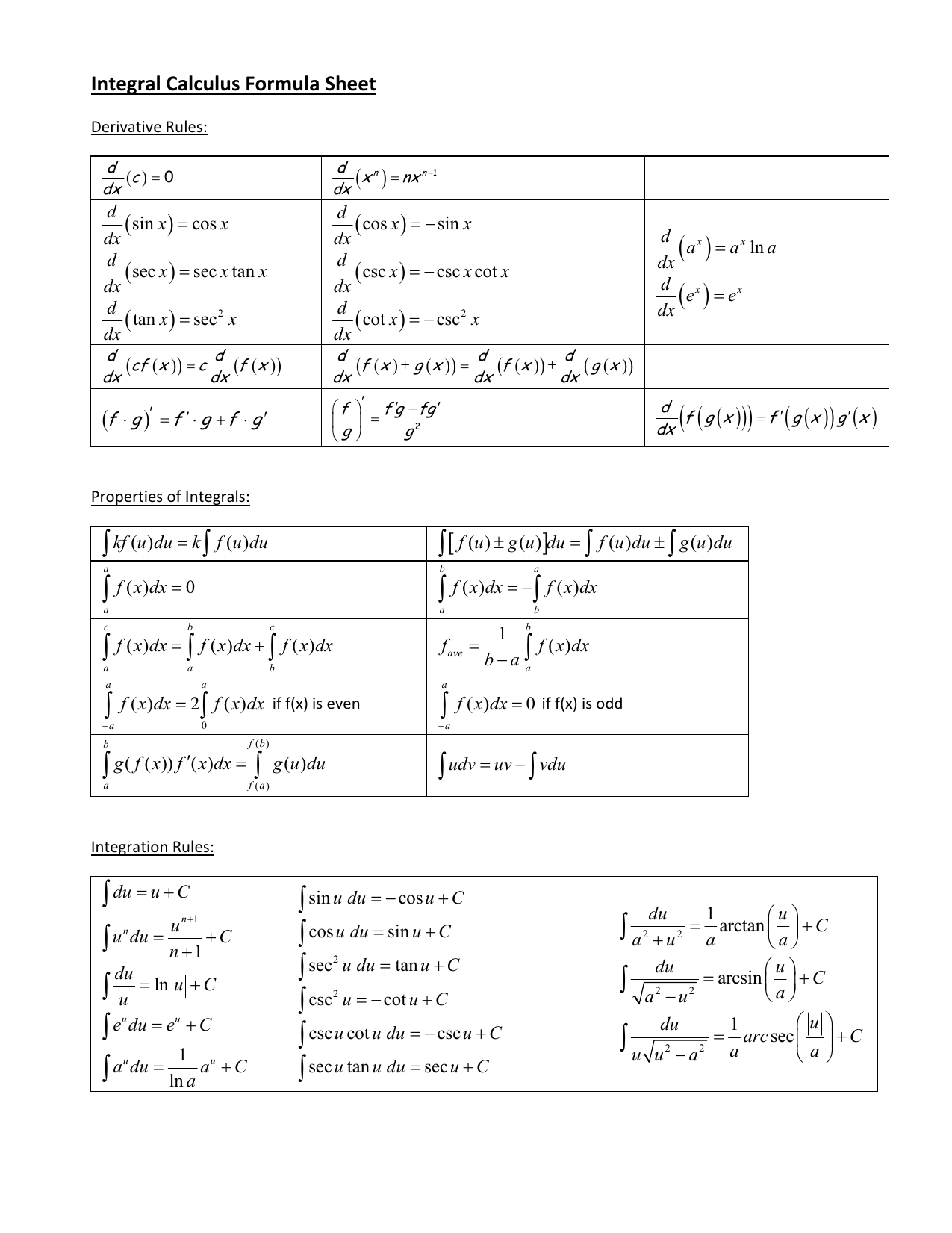
Integral Calculus Formula Sheet 0

Consider The Functions F X 2x See How To Solve It At Qanda

Let F X X2 2x 15 And G X X3 See How To Solve It At Qanda
If G X 2h X H X 2h X H X Where H X Sin X Sin Nx N R And Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community

Lesson 27 The Fundamental Theorem Of Calculus

Am 2 4 Funkcje Ich Granice I Ciaglosc Pobierz Pdf Z Docer Pl

Solved Let C Be A Constant Then If F X C Its Derivati Chegg Com

Section 6 2 Calculating Coefficients Of Generating Functions

If Y Determinant F X G X H X L M N A B C Prove Dy Dx F X

Notes 07 Studocu

Answered D Y 0 140 If Y X 1 X 2 X Bartleby

Calculus Cheat Sheet Integrals

Dany Jest Wykres Funkcji F X

Pdf C 2 Mathbb R 2 Nonnegative Extension By Bounded Depth Operators

Naszkicuj Wykres Funkcji F Oraz Wykres Funkcji G X F X Podaj Przedzialy I Monotonicznosci Funkcji Brainly Pl

1 Powtorzenie Okreslenie I Przyklady Grup Pdf Free Download

Solved 1 Use The Table Below To Find The Following Deriv Chegg Com

Limits Calculus Study Guide

Pro Plan Veterinary Diets Nf Renal Function Karma Dla Kotow Kurczak 10 X 85 G Sklep Empik Com

Biologia Zadania Przygotowawcze Do Egzaminu Z Matematyki Pdf Darmowe Pobieranie

Introduction To Antiderivatives

1060 G Fx 3 0n Au 2 3 C Ptr Hartmann Styk Sprezynowy 24 A 28 5 Mm Plaska Glowica Distrelec Polska

Reading The Definite Integral Applied To Area Business Calculus
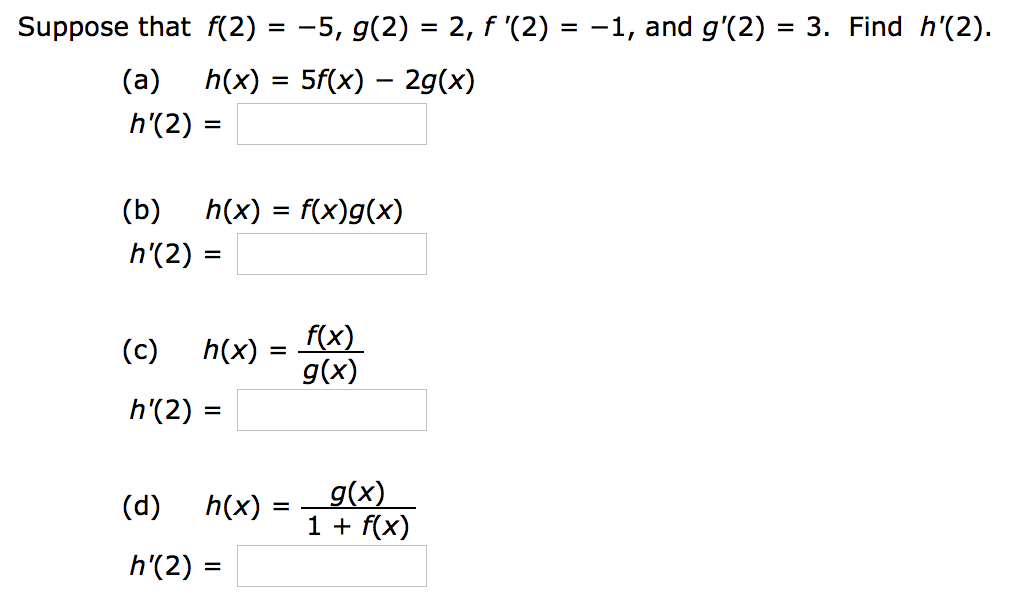
Solved Suppose That 2 5 G 2 2 F 2 1 And G 2 3 Chegg Com
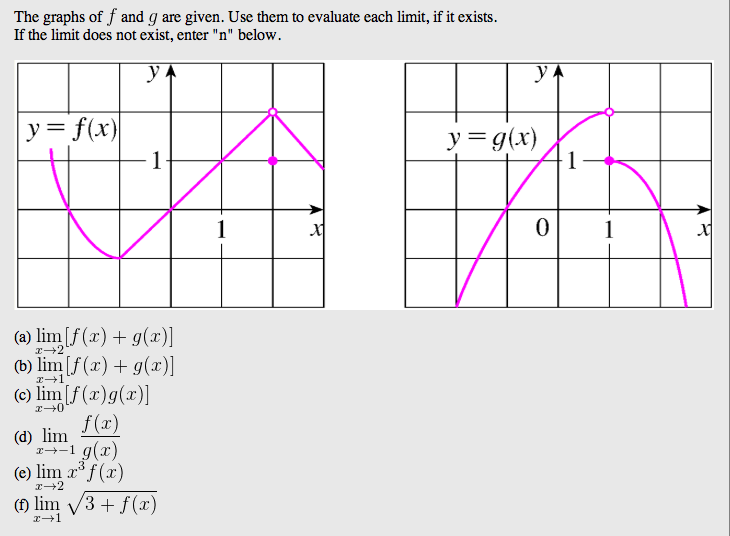
Solved The Graphs Of F And G Are Given Use Them To Evalu Chegg Com
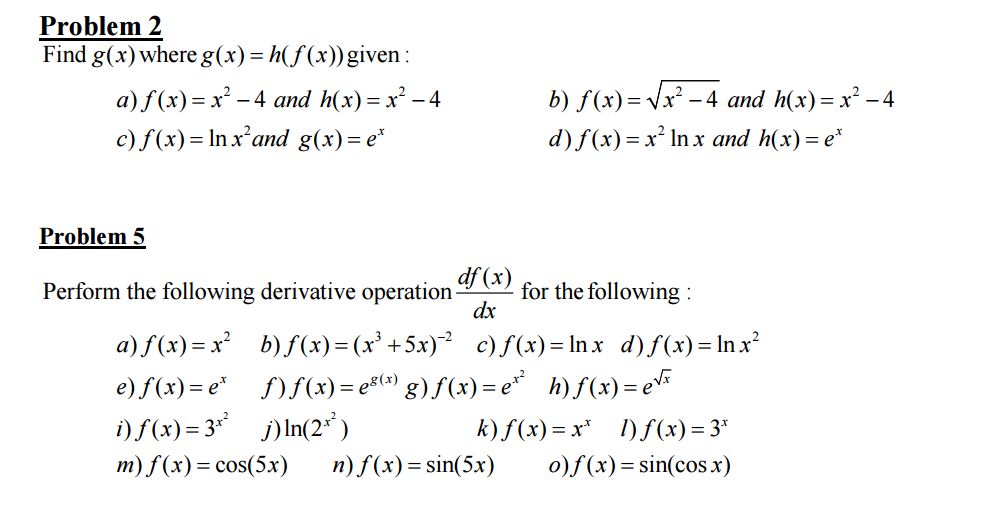
Solved Find G X Where G X H F X Given F X X 2 Chegg Com

Solved Find Each Of The Following Functions F X X 5 Chegg Com

Answered Assume F G Are Differentiable Bartleby

Rachunek Calkowy Pobierz Pdf Z Docer Pl
Let F X X 1 X N 1 N For N 2 And Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community

Solved The Chain Rule For Differentiation Is F Composite Chegg Com

If F X Is A Differentiable Function And G X Is A Double Differentiable Function Such That F X 1 And F X G X If F 2 0 G 2 0 9 Such That There Exists

Given F X And G X K F X Use The Graph To Determine The Value Of K A 3 B 1 3 C 1 3 D Brainly Com
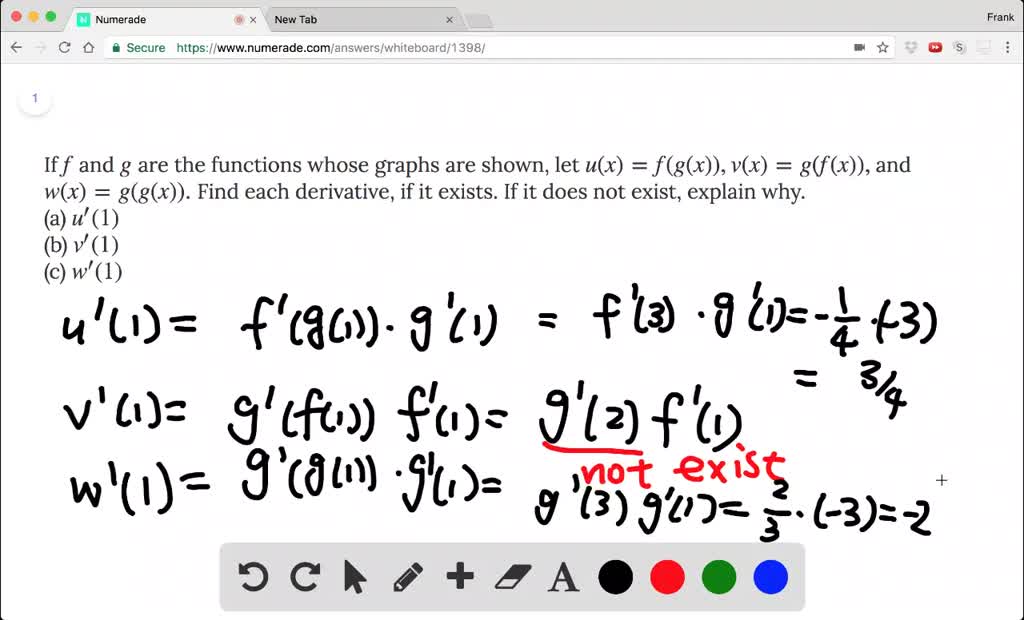
Solved If F And G Are The Functions Whose Graphs

Solved If Your Answer Is True Justify By Quoting A De Chegg Com

How To Simplify This Composition Function G X Underset N Text Times Underbrace F Circ F Circ F Circ F Circ F Circ Cdots Circ F X Mathematics Stack Exchange
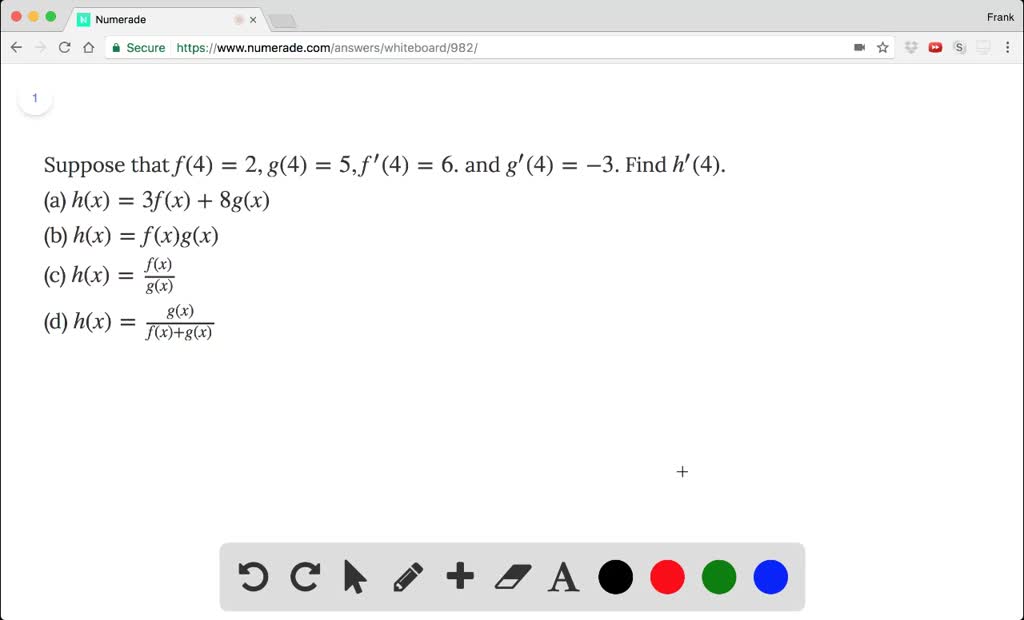
Solved Suppose That F 4 2 G 4 5 F 4 6

If Y F X G X H X L M N A B C Prove That Dy

Show That Parseval S Theorem For Two Real Functions Whose Fourier Expansions Have Cosine And Sine Coefficients An Bn And An Bn Takes The Form 1 L 0 L F X G
Ppt Algorytmy I Struktury Danych Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id

Przestrzen Funkcji Mierzalnych Cwiczenia Teoria Miary I Calki Docsity

Answered 7 7 Consider Two Functions F And G On Bartleby

If Y Determinant F X G X H X L M N A B C Prove Dy Dx F X

If Y Determinant F X G X H X L M N A B C Prove Dy Dx F X

Ax B And G X Cx

The Following Are Notations F See How To Solve It At Qanda

Fx G Punkt Magiczna Rozdzka Kijek Do Masazu Czysty Material Metaliczny Tanie I Dobre Opinie

Fx G Punkt Magiczna Rozdzka Kijek Do Masazu Czysty Material Metaliczny Tanie I Dobre Opinie
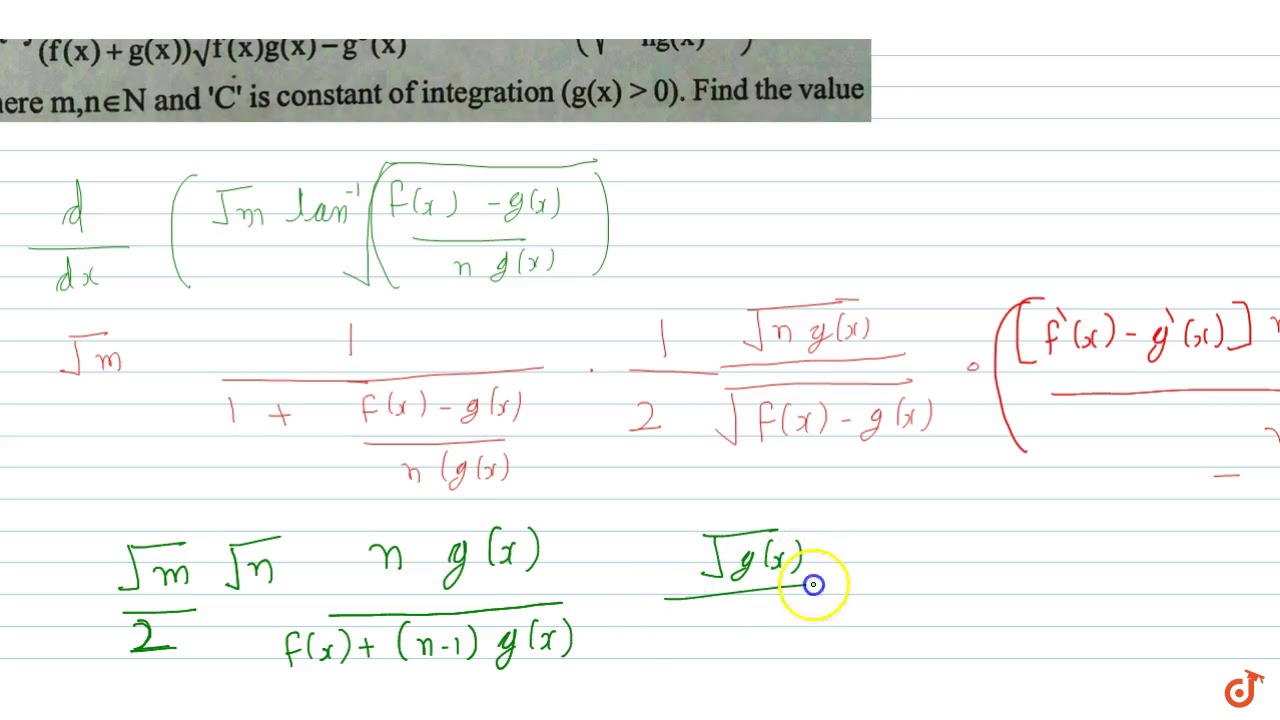
If Int F Prime X G X G Prime X F X F X G X Sqrt F X G X G 2 X D X Sqrt M Tan Youtube

Let F X G X X W H E Nx 0 And F 0 0 If G 0 G Prime
Let G X Log F X Where F X Is A Twice Differentiable Positive Function On 0 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community

Let F X Be A N Degree Polynomial Function Having N Real And Distinct Roots If G X F X 100f X Mathematics Stack Exchange

Exactly five R A B But Not Uniformly Flip Ebook Pages 1 5 Anyflip Anyflip

Additional Mathematics Functions Questions 1 Given Function F X Mx 4 X N X N If F 2 10 And F 8 4 Find A The Values Of M And N B The Ppt Download




