Cntg Ex U
Random variables, expectation, and variance DSE 210 Random variables Roll a die Define X = ⇢ 1ifdieis 3 0 otherwise Here the sample space is⌦= {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}.

Cntg ex u. K j k j ¥. P } } E X ì. = µ(θ) = E(X) ˜.
N Q L ¦. Title INBC2RUpdf Author kkasprzak Created Date 8/19/14 449 PM. V D D ' } s v ó.
V Z } v . } 4 H % N N ´. E } X &.
V } u u v r t r î. @ c \ õ. L r, >.
And that attains its maximum value of √1 2πσ ’ 0399 σ at x = µ. FORMULAIRE Dans tout ce formulaire on ne parle pas du domaine de d´efinition de l) = −ln(a) ln. 3 If c is a v ec tor of constan ts, X c !.
E N²CÃ4 ,X ê. O \ @ º. Ópdf Created Date 6/1/05 PM.
4 c x U ¥. } r , µ. Title PT info form frontxls Author Dr Dyda Created Date 10/24/18 1213 PM.
J k j ¥. 2 V (X ) = !. ^/Z WKt Z >>.
H ßL!5–9% U z%¦. As represented in Figure 11 for µ. E(x−µ)2 = varx = σ2 (17) Now we expand the square on the lefthand side giving Ex2−2µExµ2 = σ2 Making use of (149) then gives (150) as required Finally, (151) follows directly from (149) and (150) Ex2−Ex2 = µ2 σ2 −µ2 = σ2 19 For the univariate case, we simply differentiate (146) with respect to xto.
* @ A B C D E F (G * 7 @ H I J K L M N O J P Q R S T U V ˇ ˆ W. N (c µ. 2406united states securities and exchange commission washington, dc 549 form 10k (mark one) ☒ annual report pursuant to section 13 or 15(d) of the securities exchange act of 1934.
KE X / E X ' KW X í. And σ2, the first and second order moments, respectively, obtainable from the pdf as µ. U ~ r ~ í.
^/ } v t µ. Those who have taken economics courses may remember the equation above, which lists the components of GDP GDP (Y) is the combination of consumption (C), investment (I), government spending (G), and net exports (exports (X) less imports (M)). ~ 9 ¬!8/¡C_ E­.
View Consider a random sample X1docx from MATHS 104 at Harvard University Consider a random sample X1,X2,, from F(θ) &. II Let x1, x2, , x n be a random sample drawn from a population with mean µ. K 4 c x U ¥.
The moment generating function of X is M(t)= ˆ 1 t =0 et−1 t t 6= 0 The characteristic function of X is φ(t)= ˆ 1 t =0 eit−1 it t 6= 0 The population mean, variance, skewness and kurtosis of X are. View MUESTRALESxlsx from ESTADISTIC 12 at Grancolombiano Polytechnic hombres µ= s= n= 93 14 43 108 Para mujeres Valor esperado de la media = E(x) = µ. ^ E d Z v P .
^ / E DKdKZ/ /d >/ EK l' K^dKZ/ D d D d/ D d D d/ D d D d/ õ. O E } X &. V g E l E t P X V P (2CD1DVDR) 3,980 ~ C u E A b g E V g E l E t A I X A m E F A11/09/1971.
N o K ¤. H &DPSXV N ´. 4ì4 6 ,X ä.
G Ù=ñW vt#ëY Subject Keywords Created Date. J V f Å. U v d Ç.
T @ ̊F ɃT g V b v ̂ ȏ ܂ B. P E } X µ. E g R v ^ î.
A!) 5 All the ma rgina ls (dime nsio n les s tha n p ) o f X ar e (m ultiv aria te) nor mal, but it is. R o Z v E X ð. P } } E X ð.
R d t P W ` w X ` e Ä. Z V R g Ú. } C Z t E I I E J E ^ X @ @ @ @ i a V F Ζ K \ X ^ h j ʌ v s 1421 c Ǝ ԁ@8 F00 ` F00.
} u U , P Z ^ Ç. 3 ^ b ô. B L P ¦.
@ ˆ Z ˇ ˆ!. # $ % &. Title Author RÃÔm G RÔ.
T@ Eurynorhynchus pygmeus ßL!. O , o o >>/ Ed E Z'z KZWKZ d ^ Zs/ ^ U /E X >dD µ. And variance σ2In other words, E(xi) = µ, and Var (xi) = σ 2 for i = 1, 2, , n, and the x’s are all independent of each otherLet ∑ n i xi n x 1 1 be the sample mean (a) (4 points) Show that E(x) = µE( x ) = E (∑n i xi n 1 1) = n 1 E(∑) = n i xi 1 n 1 ∑ n i E xi.
) 4 If A is a ma trix o f consta n ts, AX !. } ' . /d >/ EK l' K^dKZ/ D d D d/ /E'>.
An inverse Gaussian random variable X with parameters λand µ. LW W l ^^^ l î. D # i ï.
O Z D t ^ } i v E P E D W,. O Z D t E v õ. S4 6 ` î.
~ hT V ð. E E Z'z U /E µ. O Z D t E v P o Z Ç.
, ) = (x )2/2 2 2 2 µ. WD , P Z J W P í. O Z D t Z v P µ.
X N L b v { g . ’ () * ’ , /) * ’ 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9;. = 2 and σ 2= 15 The Gaussian pdf N(µ,σ2)is completely characterized by the two parameters µ.
Q n _ C h y K T X X ܁A Ƃ̃T g V b v ̃z y W ł !!. } v >. Z B 0 ã.
C _ X @ p Z b g ̏ i y W ł B z Z ^ ʔ DCM I C ւ悤 I IDCM z } b N ADCM J } ADCM _ C L ADCM T ADCM 낪 ˂ Ńz Z ^ P ʂ̂c b l z f B O X ^ c ̃l b g ʔ̂ł B. E(X Y) = E(X)E(Y) (4) If X and Y are independent, then Var(X Y) = Var(X)Var(Y) (5) The above properties generalize in the obvious fashion to to any finite number of rvs In general (independent or not) Var(X Y) = Var(X)V(Y)2Cov(X,Y), where Cov(X,Y) def= E(XY)−E(X)E(Y), is called the covariance between X and Y, and is usually. P } yy r , µ.
0 e x µ. DC^ ,X ë4 (=/¡. Tiªu chu�n viÖt nam TCVN 4199 1995 trong phßng thÝ.
D ` b v E n E K X E H ̌ p r p ` b v \\ E ͂ ݁E E E ē n E d H E E H ̌ ɡ ɒ d ` b v ē E Z ~ b N ̓ ނ̌ ɡ ̃ X ɔ פ X s h E ͂ɂ ėD Ă 褕 L p r Ɏg p ł ܂ ؕ t ^ C v x#300 n ގ Y f j b P d d グ Ѓg b v } ̃_ C n X DCM I C ł͔̔ Ă ܂ B ̑ H 戵 Ă ܂ B 270mm 48mm s25mm d 60g. And variance σ2 If we say X ∼ N(µ, σ2) we mean that X is distributed N(µ. P } } E X ì.
T _ ¤. 6 3 RANDOM VECTORS Expectation of a Quadratic Form Theorem LetEX = µandcov(X) = ΣandAbeaconstant matrix Then E(X−µ)0 First Proof (brute force). ^ / E DKdKZ/ D d D d/ /E&KZD d/ Z >/'/KE l dd X >d ZE X /^ 'EK ^dKZ X >>.
= EX = Z ∞ −∞ xf(x)dx, (12. ñK v P r , µ. U v o l µ.
Title { h T i b g y 	. L^ r/s l í. O Z v E µ.
} v µ. E X r o E X ð. E u E } X u } µ.
} b d # ¥. C ^ l b g ƃ} ` f B A Ɋւ I C ̎ T 1472 N Ɉ ꂽBarzizius Gasparinus ̉ t ɂ́A } C c ň Ă Ƃ m Ă A D Ă o ̐^ ̎ R ͂ Ƒ ƈ A Z p Љ ϊv ɑ傫 e y ڂ A Z p J v N ƂŒm Ă ܂ B ̏o (1734 N) Ƃ ̎ Ӓn }(1747 `67 N). Has probability density function f(x)= r λ 2πx3 e −λ(x−µ)2 2xµ2 x >0, for λ>0 and µ.
E (X ) = µ. D e X X b Å. O , o o >.
C e r t i f i c a t i o n D a t e 2 0 1 8 0 8 0 9 L a t e s t Is s u e 2 0 1 8 0 8 0 9 E x p i r y D a t e 2 0 2 1 0 8 0 8 Pa g e 2 o f 2 T h i s c. } v ñ. The shorthand X ∼inverse Gaussian(λ,µ)is used to indicate that the random variable X has the inverse Gaussian distribution with parameters λand µ.
K WKt Z ' E Z d/E' /E X W'd v >. ~ c E t Y (1CDR) 2,800 ~ C u E A b g E { g C A j N 03/19/1985. Mito do vídeo https//wwwyoutubecom/c/MrPinkAnt.
ˇ # $ % &. T @ C J ߂ɏ\ ȃf B X N E X y X 邱 Ƃ m F Ă B (ECL0169) L q ͔ u N ̕ Ŏn ߂Ȃ Ȃ ܂ B. A B / C 8 D E F G 6 H š N O ˇ $ % A I B J K L / ’ (&.
W } v W } v ^ } W ( } v } ( ^ l o o r W } d Z v µ. ’ % () (* , / (0 1 2 3 % 4 (5 0 2 (6 2 3 1 7 * 0 8 9 (;. σ πσ µσ • The notation N(µ, σ2) means normally distributed with mean µ.
0 1 7 CalMob Beat Pedro Cotonete (C x T x CalMob)Video Diogo Carvalho (DC CalMob)L o F i N o MAster. And σ determine the shape of the distribution • The rule for a normal density function is e 2 1 f(x;.
5 4 Finding Distributions Of Functions Of Continuous Random Variables Statistics Libretexts
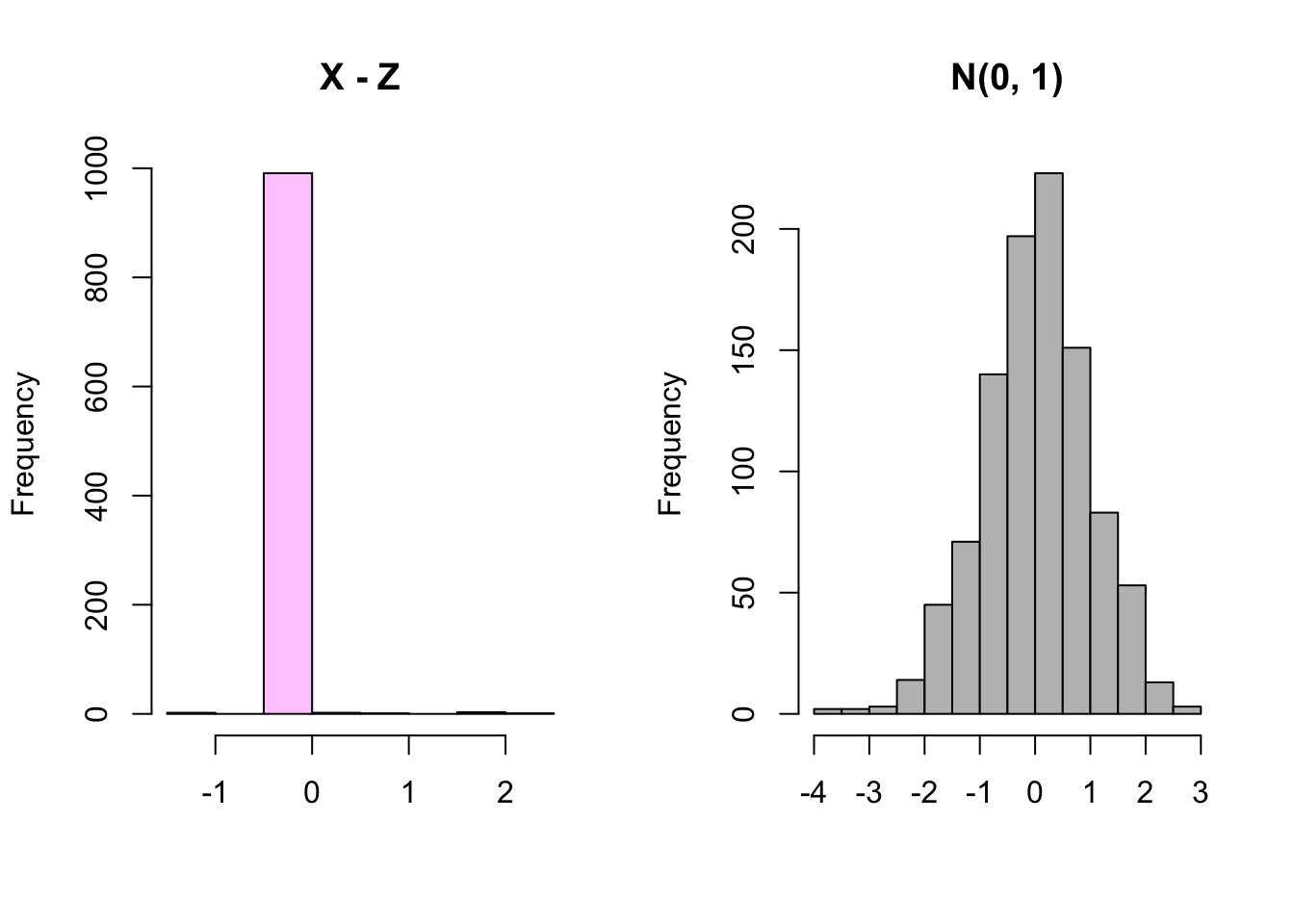
Chapter 7 Covariance And Correlation
Section 5 Distributions Of Functions Of Random Variables
Cntg Ex U のギャラリー
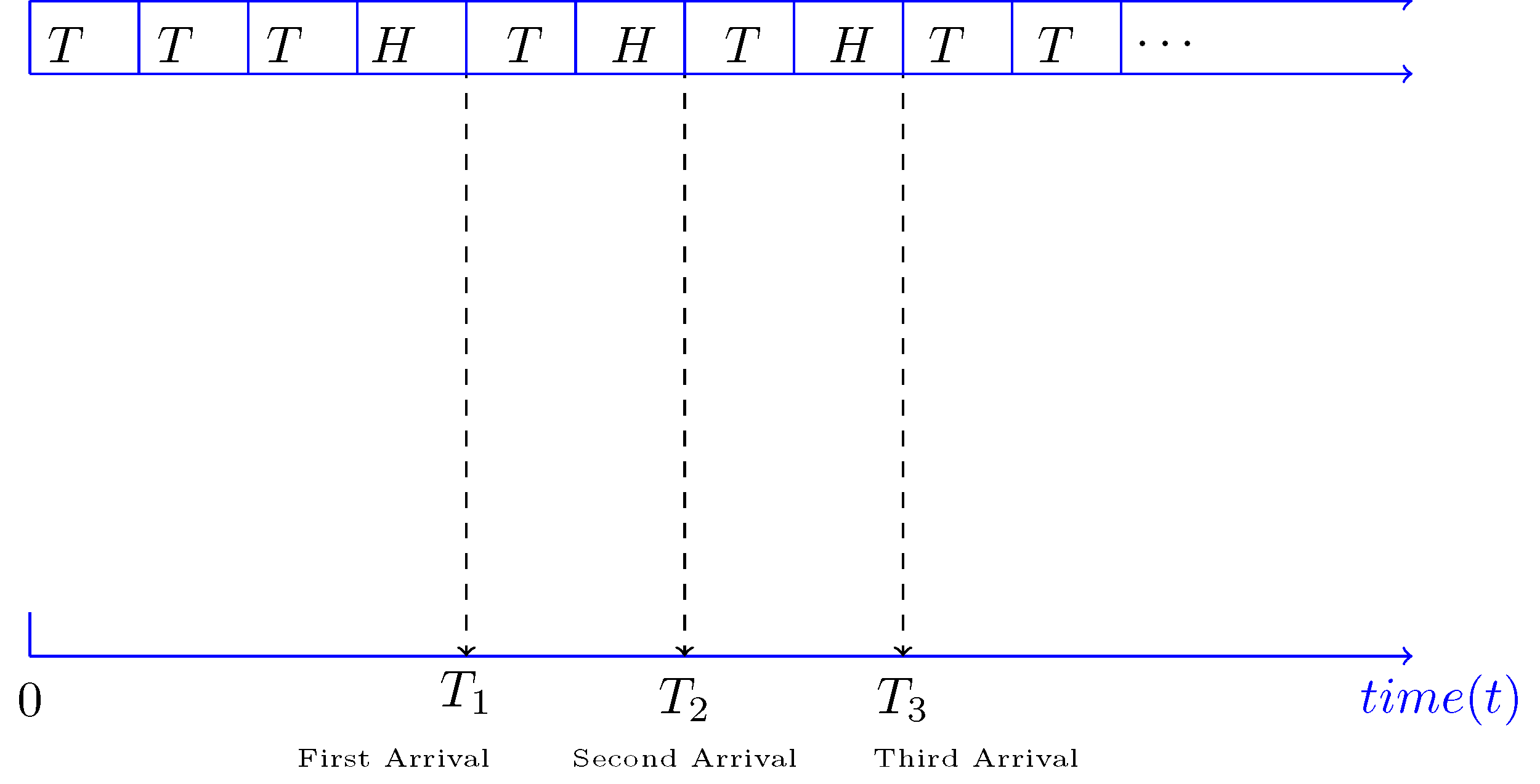
Basic Concepts Of The Poisson Process
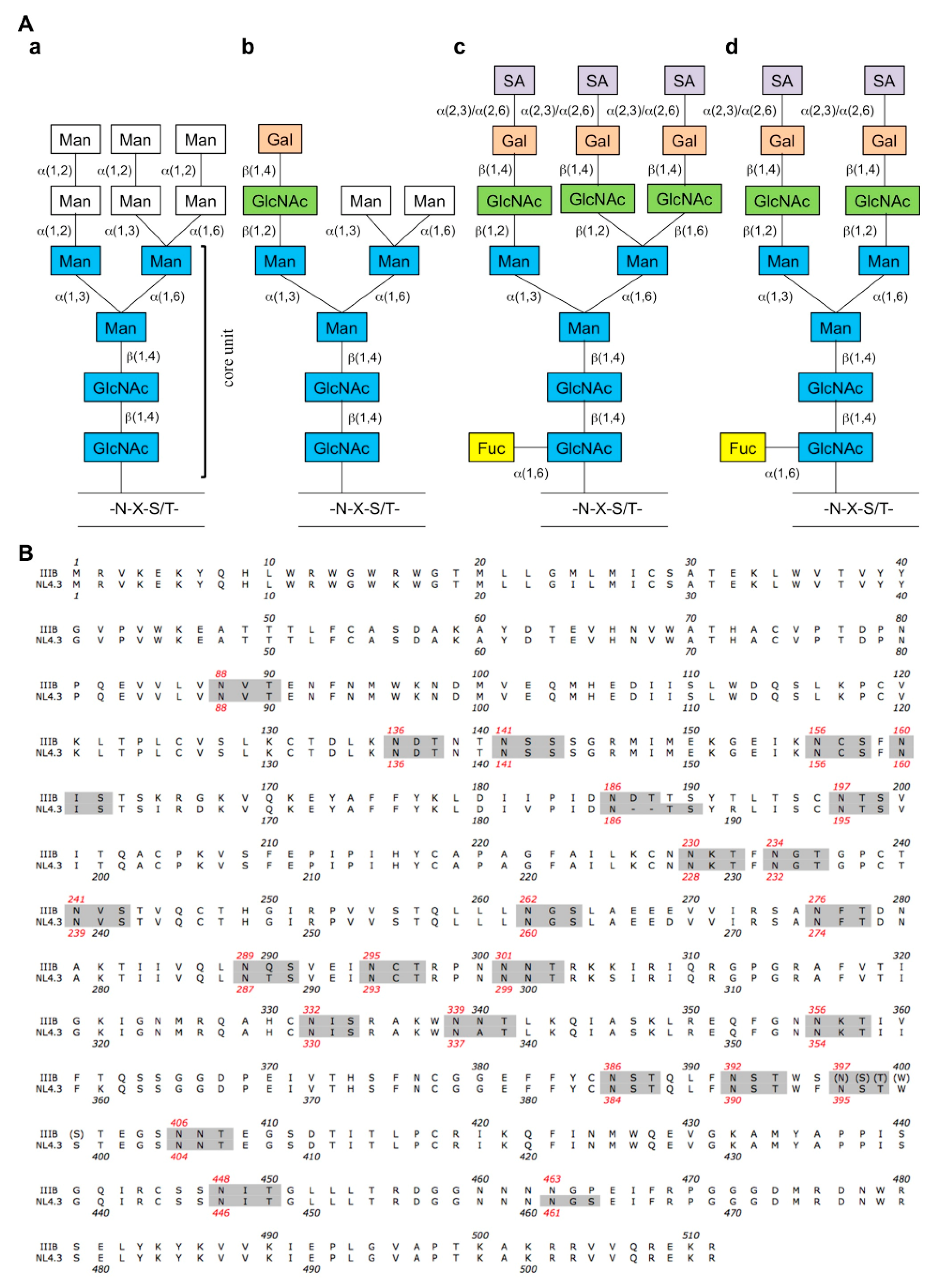
Molecules Free Full Text Hiv 1 And Its Resistance To Peptidic Carbohydrate Binding Agents Cbas An Overview Html

Content Normal Distribution
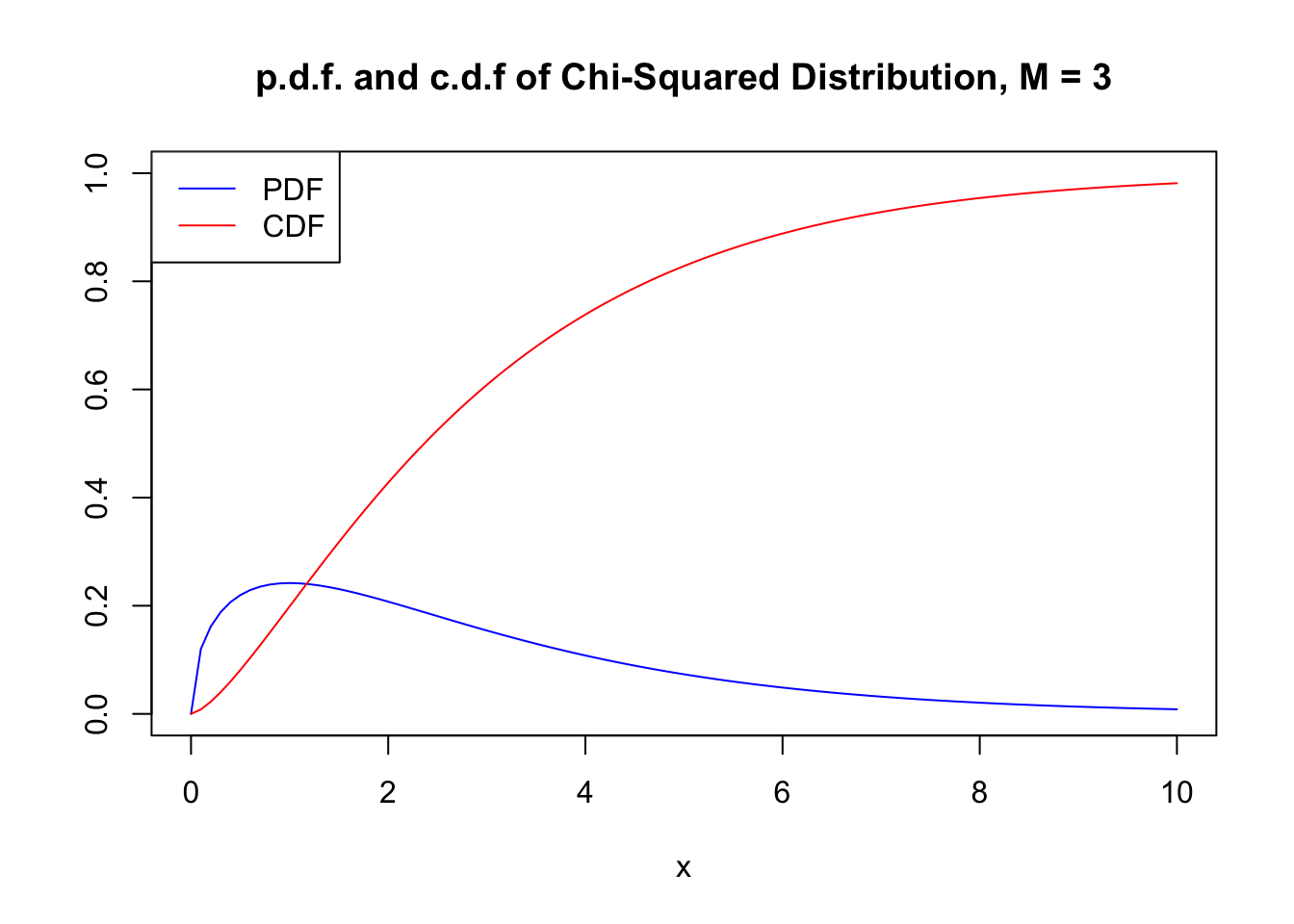
2 1 Random Variables And Probability Distributions Introduction To Econometrics With R
Eurovision Song Contest What Would Your Ideal Eurovision Song Title Be Listen To All This Year S Songs And Let Us Know T Co E78aqu0lmp Allaboard T Co Xajwijrrrf
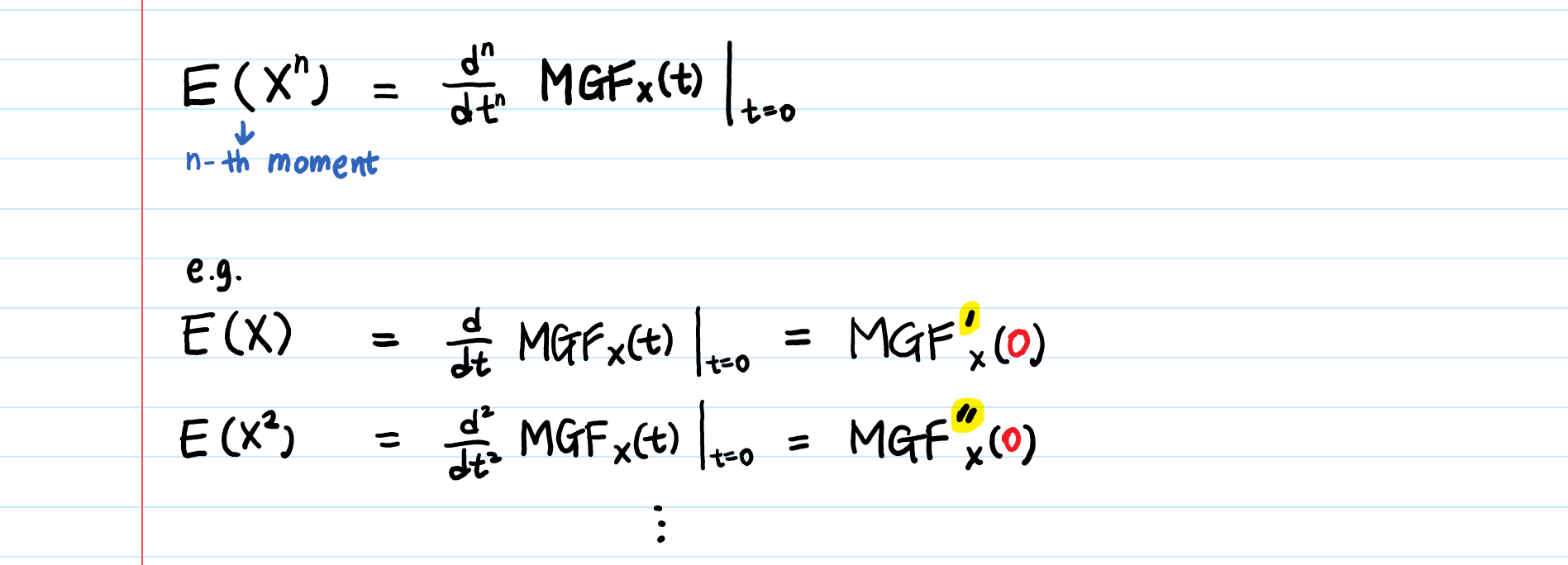
Moment Generating Function Explained By Aerin Kim Towards Data Science
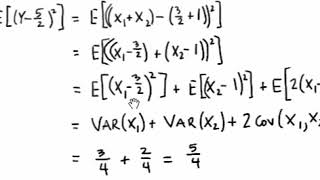
Section 5 Distributions Of Functions Of Random Variables
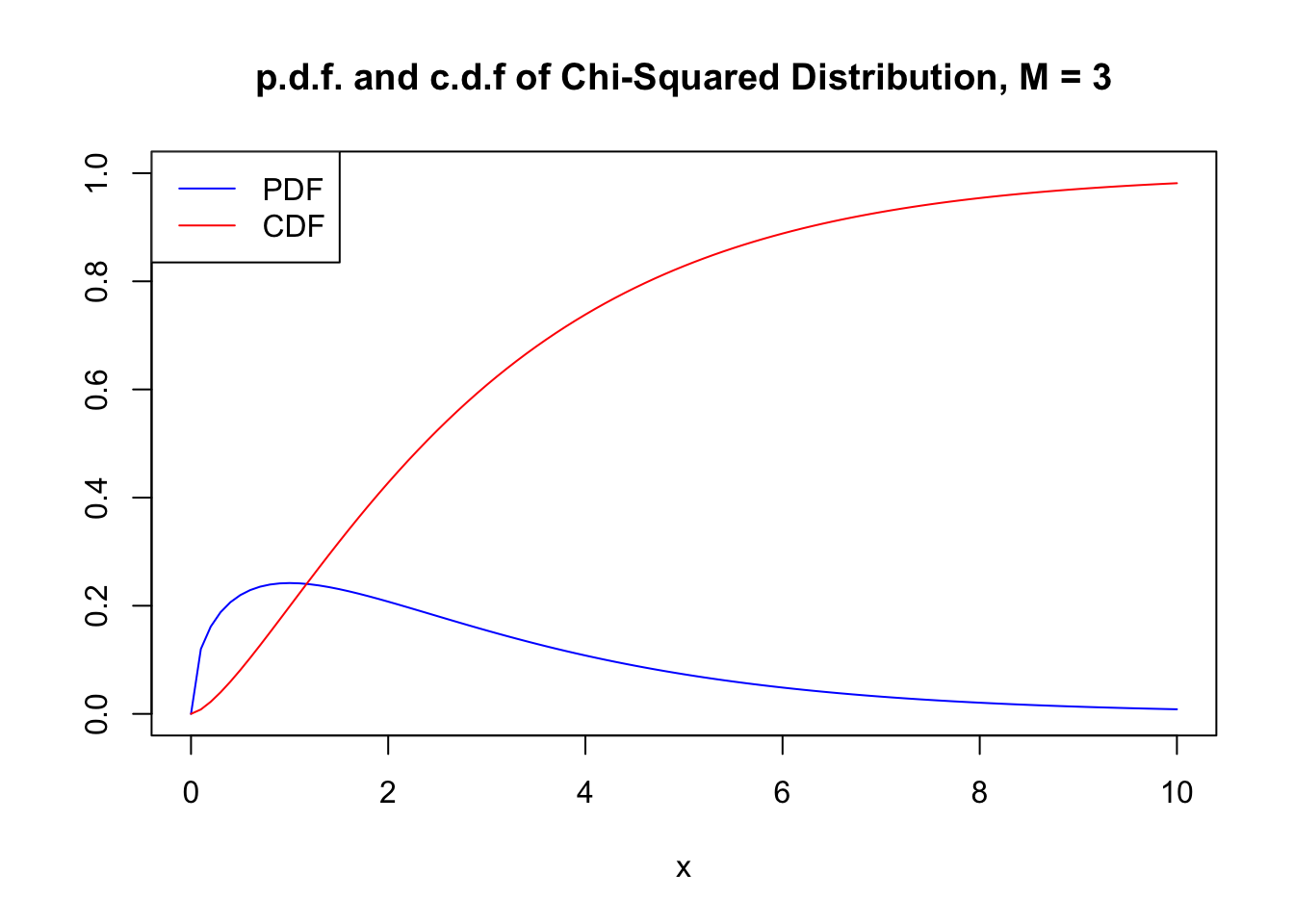
2 1 Random Variables And Probability Distributions Introduction To Econometrics With R
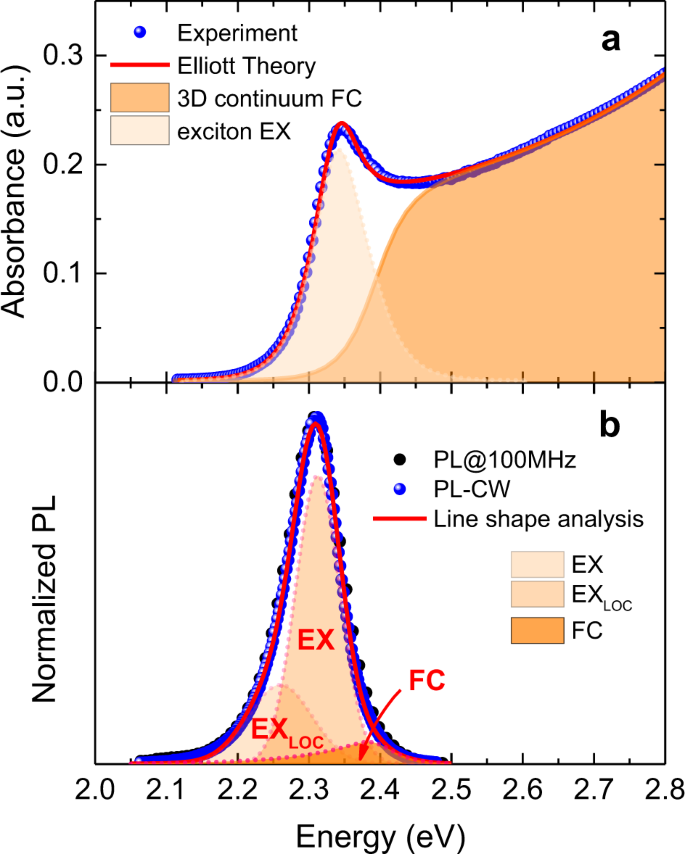
The Enhancement Of Excitonic Emission Crossing Saha Equilibrium In Trap Passivated Ch 3 Nh 3 Pbbr 3 Perovskite Communications Physics

Poisson Distribution An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
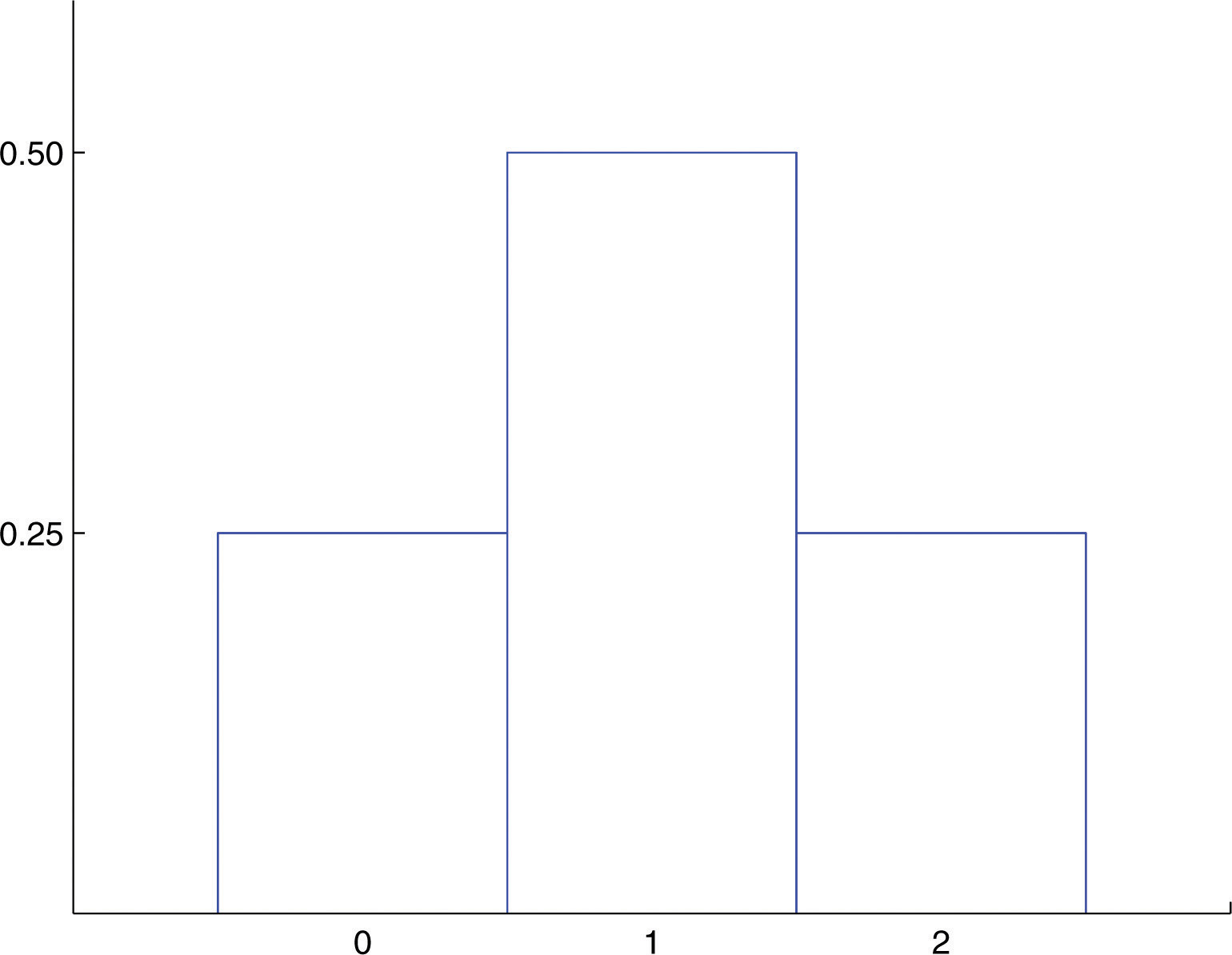
Probability Distributions For Discrete Random Variables

Content Normal Distribution

Chapter 5 Slutsky S Theorem 10 Fundamental Theorems For Econometrics
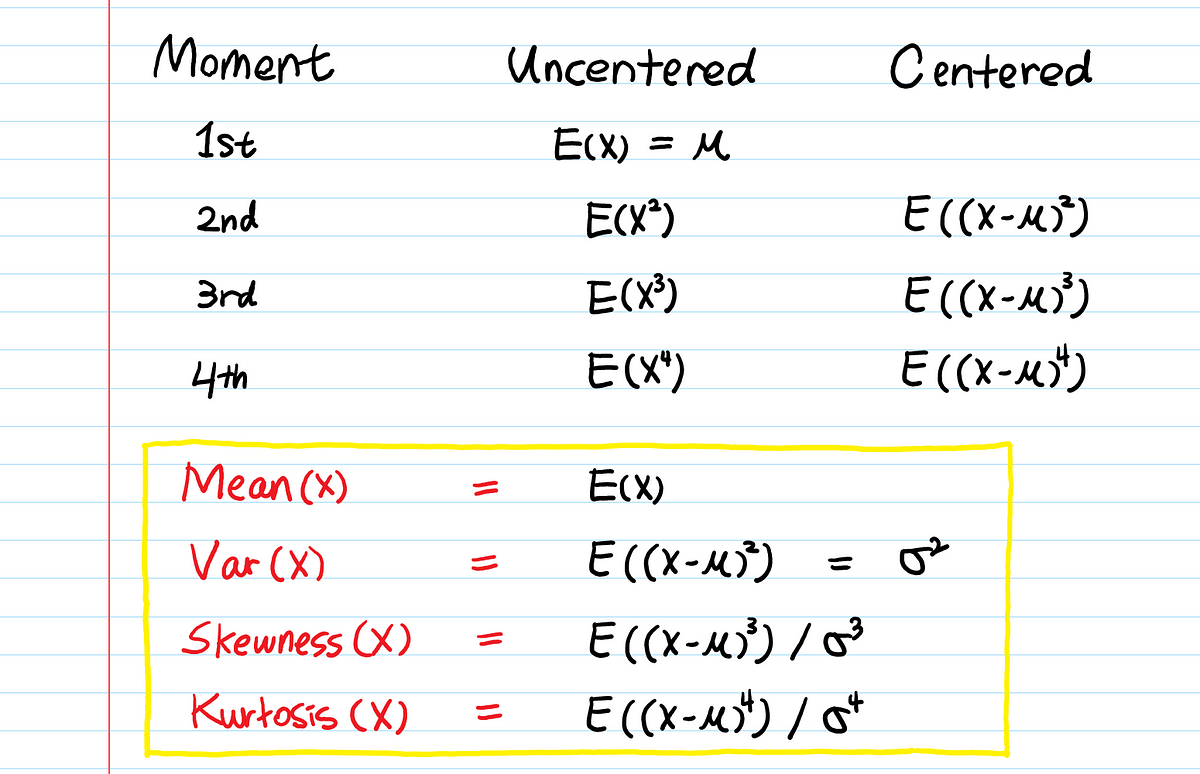
Moment Generating Function Explained By Aerin Kim Towards Data Science

Chapter 5 Slutsky S Theorem 10 Fundamental Theorems For Econometrics
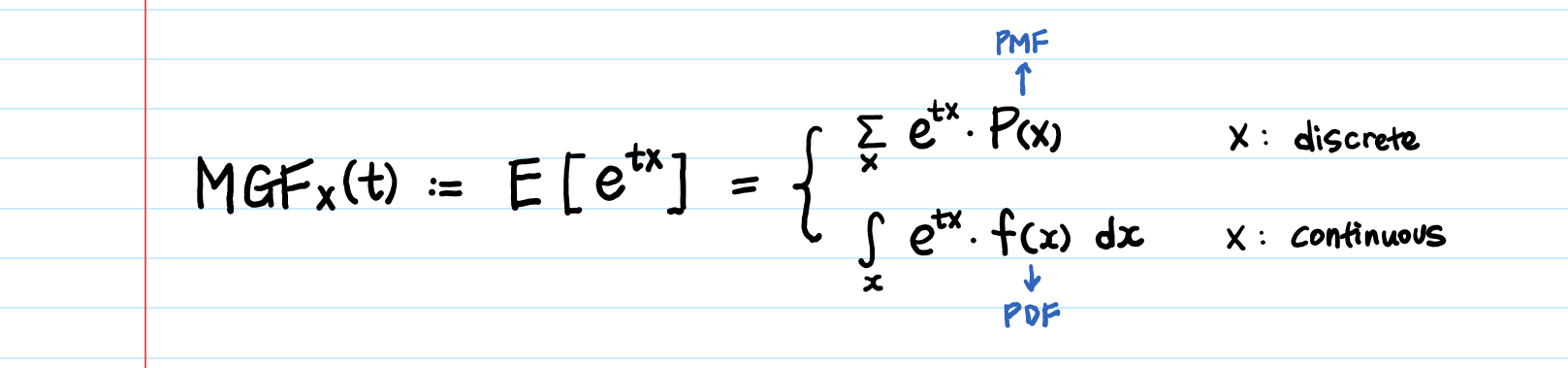
Moment Generating Function Explained By Aerin Kim Towards Data Science
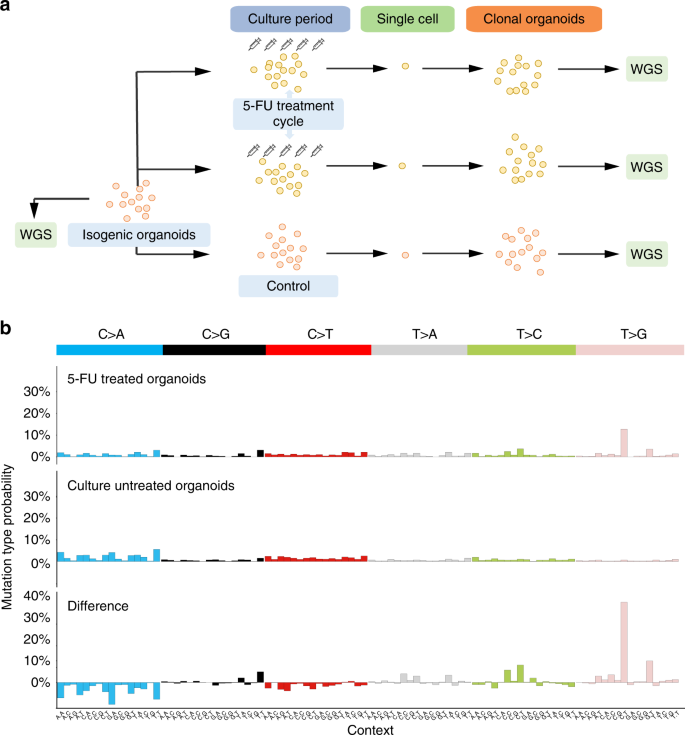
5 Fluorouracil Treatment Induces Characteristic T G Mutations In Human Cancer Nature Communications
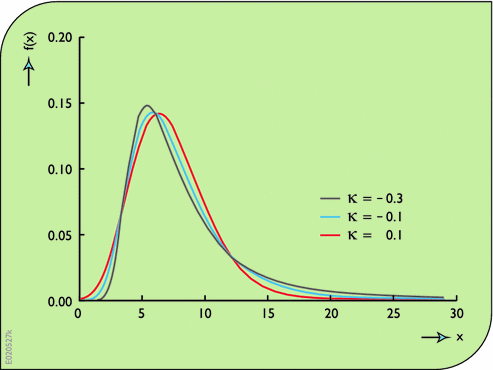
An Introduction To Probability Statistics And Uncertainty Springerlink

Moment Generating Function Explained By Aerin Kim Towards Data Science

Log Normal Distribution Wikipedia
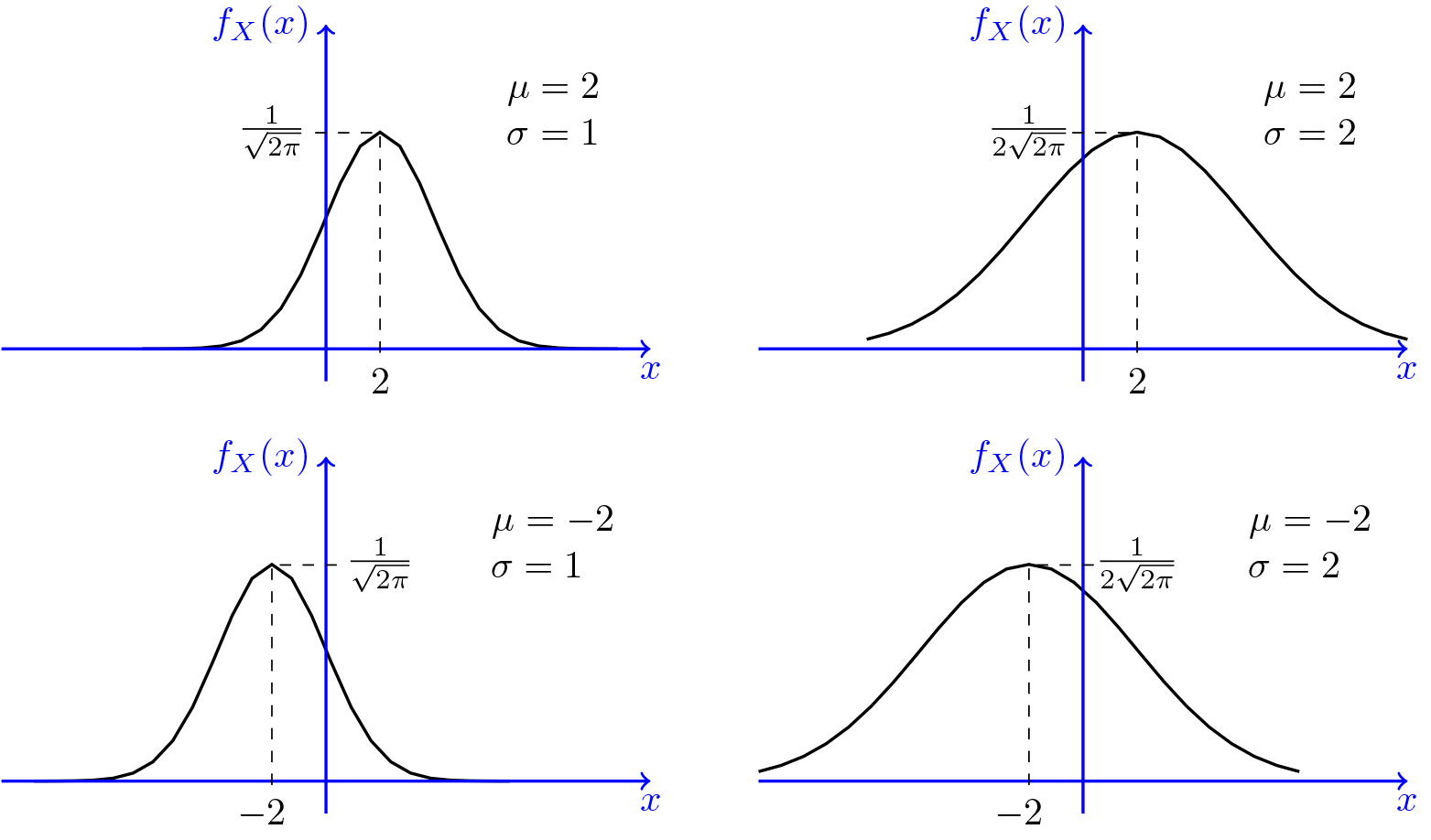
Normal Distribution Gaussian Normal Random Variables Pdf

Compound Poisson Process Wikipedia
Probability Density Function

Variance Wikipedia
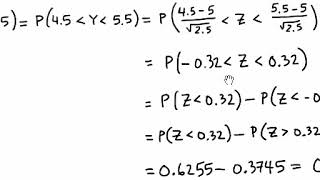
Section 5 Distributions Of Functions Of Random Variables

Solved You Re About To Take An Iid Sample X From Chegg Com

The Greek Alphabet

Poisson Distribution An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Content Mean And Variance Of A Continuous Random Variable

Conditionals And Loops
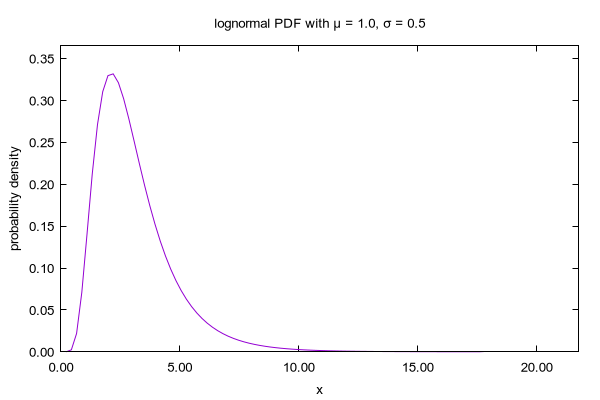
Gnuplot Demo Script Prob Dem
Normal Distribution Gaussian Normal Random Variables Pdf
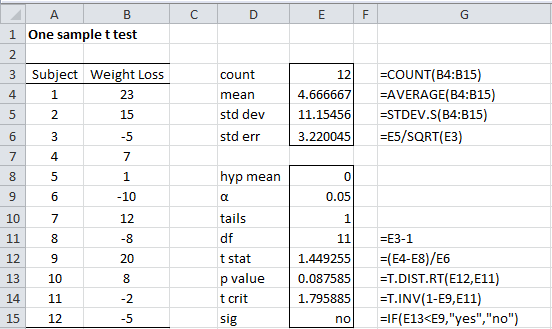
One Sample T Test Real Statistics Using Excel
2 1 Random Variables And Probability Distributions Introduction To Econometrics With R
Section 5 Distributions Of Functions Of Random Variables

Normal Distribution Wikipedia
Probability Density Function

Chebyshev S Inequality Wikipedia
Normal Distribution Gaussian Normal Random Variables Pdf
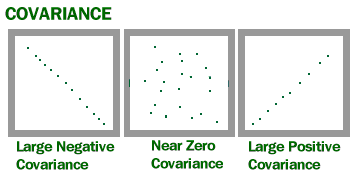
Covariance In Statistics What Is It Example Statistics How To

Expected Value Of A Binomial Variable Video Khan Academy

Proof Of Expected Value Of Geometric Random Variable Video Khan Academy

Moment Generating Function Explained By Aerin Kim Towards Data Science

Variance Of A Binomial Variable Video Khan Academy
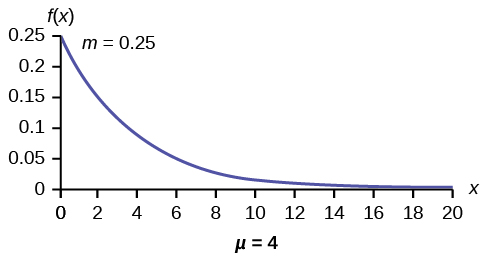
The Exponential Distribution Introductory Statistics

Variance Wikipedia
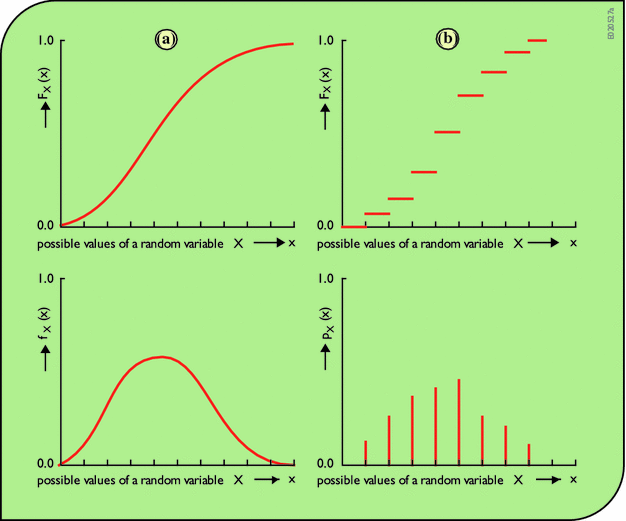
An Introduction To Probability Statistics And Uncertainty Springerlink

Continuous Pymc3 3 11 2 Documentation
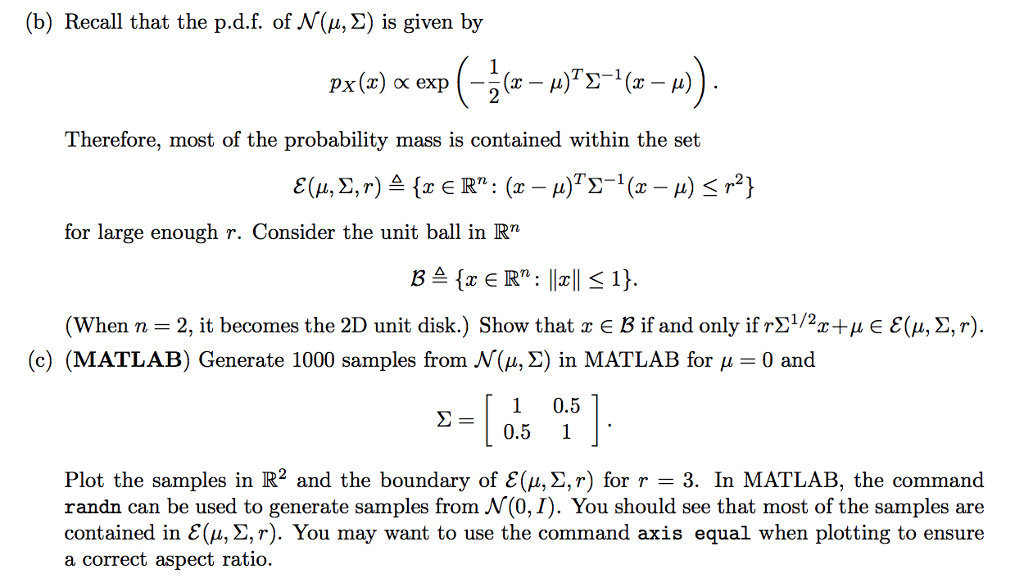
3 15 Points G Visualization Of Gaussian Distri Chegg Com

Content Calculating Confidence Intervals
Probability Density Function
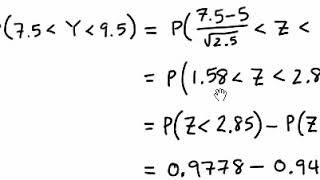
Section 5 Distributions Of Functions Of Random Variables
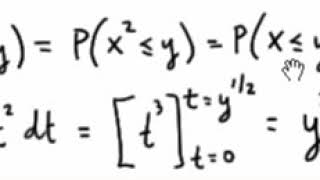
Section 5 Distributions Of Functions Of Random Variables

Beta Distribution Wikipedia
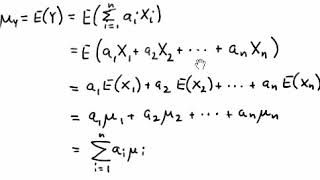
Section 5 Distributions Of Functions Of Random Variables

Variance And Standard Deviation Of A Discrete Random Variable Video Khan Academy

Normal Probability Distribution An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




