Air Ideal Gas Constant
Define gas constant gas constant synonyms, gas constant pronunciation, gas constant translation, English dictionary definition of gas constant n Symbol R A constant, equal to 14 joules per kelvin, 0006 liter atmospheres per mole.
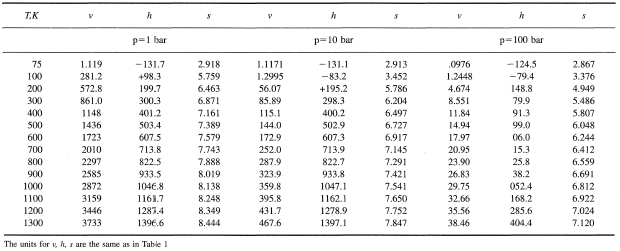
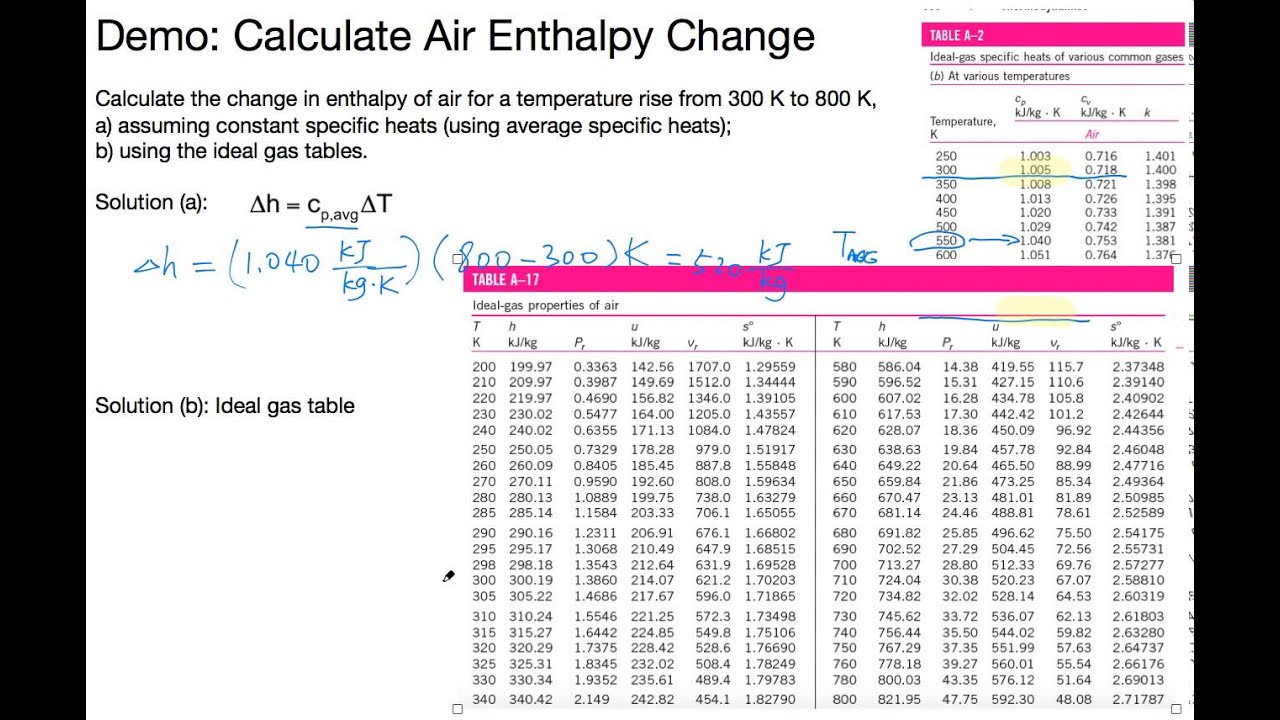
Air ideal gas constant. May 13, 21 · For an ideal gas, the equation of state is written p * V = R * T where R is the gas constant The heat transfer of a gas is equal to the heat capacity times the change in temperature;. May 08, 14 · The Gas Constant, R, from the Ideal Gas Law is Joules / (moles • Kelvin) The gas constant (also known as the molar, universal, or ideal gas constant, denoted by the. 2 Table of Contents Table A1SI Polynomial Constants for c P (kJ/(kmole∙K)) 3 Table SI Specific Heats for Ideal Gases in SI Units 4 Table A3SI Ideal Gas Properties of Air in SI Units 10.
Where is the specific heat (also called heat capacity) at constant pressure, while is the specific heat at constant volume The specific heat, in turn, is the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of the gas by one degreeIt is derived in statistical thermodynamics that, for an ideal gas, we have , where is the ideal gas constant (introduced in Eq. Jan 07, 19 · The gas constant or R is an essential constant in the ideal gas law Discover the definition and value of the gas constant. = , where k is a constant Ideal Gas Law This law combines the relationships between p, V, T and mass, and gives a number to the constant!.
Mar 12, 18 · Mass 1 lb= g 1 lb= kg 1 lb 7000gr 1 kg= lb 1ton=00lb 1 longton= 2240lb 1 tonne lb 1 tonne 1000kg 1lb=16oz. Table A–1E Molar mass, gas constant, and criticalpoint properties Table A–2E Idealgas specific heats of various common gases Table A–3E Properties of common liquids, solids, and foods Table A–4E Saturated water—Temperature table Table A–5E Saturated water—Pressure table Table A–6E Superheated water Table A–7E Compressed liquid water Table A–8E Saturated ice–water vapor. N is the amount of substance, measured in moles;;.
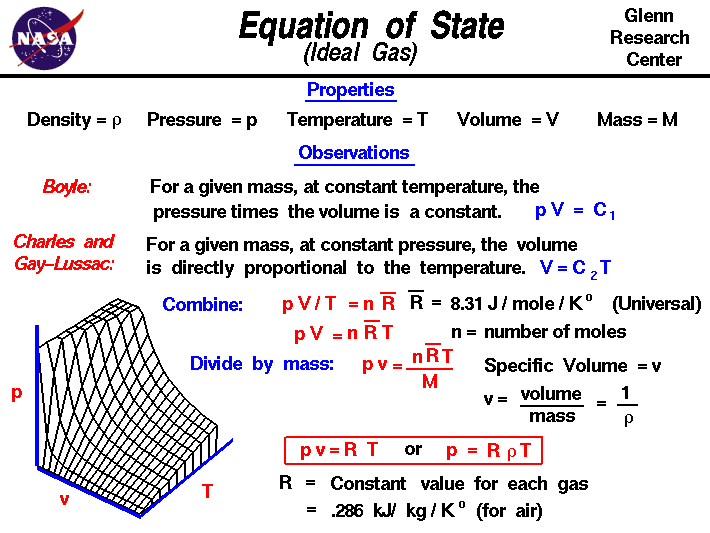
The gases obeying this equation are called Ideal Gases The gas constant R (Ideal Gas Law ) is given by (1 18) where is called the universal gas constant and is equal to 14 J/kgK For air the gas constant R = 2869 J/kgK (c) Aerospace, Mechanical & Mechatronic Engg 05. Ideal gas properties of air are provided in Table E1 The specific internal energy provided in Table E1 is computed by integration of the ideal gas specific heat capacity at constant volume. Where p is the absolute pressure, V is the volume, m is the mass, T is the absolute temperature (units in Kelvin or Rankine) and R is the gas constantKelvin is related to Celsius by T K = T C and Rankine is related to Fahrenheit byT R = T F This equation is also referred to as the perfect gas law or the equation of state for an ideal gas.
To express nonideality, the z factor is added as below to the ideal gas equation Pv=znRt Where P is pressure, v volume, n number of moles, r a constant and T temperature For an ideal gas z is effectively equal to exactly 1 and falls out of the. Potential energy effects and modeling air as an ideal gas with constant c p = 1008 kJ/kg∙K, determine (a) the velocity of the air at the inlet, in m/s (b) the temperature of the air at the exit, in K (c) the exit crosssectional area, in cm2. In differential form dQ = C * dT If we have a constant volume.
Oct 02, 13 · The Ideal Gas Equation Before we look at the Ideal Gas Equation, let us state the four gas variables and one constant for a better understandingThe four gas variables are pressure (P), volume (V), number of mole of gas (n), and temperature (T) Lastly, the constant in the equation shown below is R, known as the the gas constant, which will be discussed in depth. The ideal gas equation enables us to examine the relationship between the nonconstant properties of ideal gases (n, P, V, T) as long as three of these properties remain fixed For the ideal gas equation, note that the product PV is directly proportional to T This means that if the gas’ temperature remains constant, pressure or volume can. A cubic metre of air contains 0906 kg of nitrogen of specific gas constant 297 J/(kg K), 0278 kg of oxygen of specific gas constant 260 J/(kg K) and 0015 kg of argon of specific gas constant 8 J/(kg K) What will be the total pressure at °C?.
1 Ideal Gas Law It is convenient to express the amount of a gas as the number of moles n One mole is the mass of a substance that contains 6022 1023 molecules (N A, Avogadro’s number)n= m=Mwhere mis the mass of a substance and Mis the molecular weight. To find any of these values,. Jul 02, 19 · The variable \(R\) in the equation is called the ideal gas constant Evaluating the Ideal Gas Constant The value of \(R\), the ideal gas constant, depends on the units chosen for pressure, temperature, and volume in the ideal gas equation It is necessary to use Kelvin for the temperature and it is conventional to use the SI unit of liters for.
The ideal gas law is pV = nRT , where n is the number of moles, and R is universal For air, one mole is 27 g (=0027 kg), so we can do a unit conversion from moles to kilograms = 14 ∙ × 1 0. Mar 09, 14 · The ideal gas equations can be used to work out how much air inside a cake will expand (though it's unlikely to be used for that) but it also applies to plenty of other situations. 21 where p is pressure (Pa = kg m –1 s –2), V is the volume (m 3), N is the number of moles, R* is the gas constant (14 J K –1 mole –1), and T is the temperature (K) Note also that both sides of the Ideal Gas Law equation have the dimension of energy (J = kg m 2 s –2).
R is the ideal gas constant;. The Ideal Gas Law express the relation between pressure, temperature and volume in an ideal or perfect gas The Ideal Gas Law expessed by the Induvidual Gas Constant The Ideal Gas Law can be expressed with the Individual Gas Constant as p V = m R T (4). The universal gas constant(Ru) is, as its name implies, universal, ie the same regardless of the gas being considered The ideal gas lawin terms of Ruis where P is the absolute pressure of the gas, Vis the volume occupied by the gas, n is the number of mols of the gas, and T is the absolute temperature of the gas.
May 19, 21 · Air behaving as an ideal gas enters a compressor followed by a constant pressure heat exchanger with the properties and volume flow rate listed in the figure Do NOT assume constant specific heats If the compressor has an isentropic efficiency of %, determine (a) 4 pts) The mass flow rate through the system (lbm/s), (b) 8 pts. V is the volume of the gas, measured in m³;;. May 10, 21 · The gas constant used by aerodynamicists is derived from the universal gas constant, but has a unique value for every gas p * v = R * T If we have a constant pressure process, then p * delta v = R * delta T.
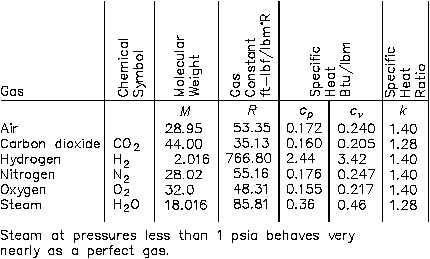
The Ideal Gas Constant Author John M Cimbala, Penn State University Latest revision, 06 January 14 Introduction Students are often confused by the units of the ideal gas constant. Mimic the behavior of an ideal gas at low pressures and high temper atures because the mixture volume is much larger than the volume of the molecules making up the mixture. TABLE A–2 Idealgas specific heats of various common gases (a) At 300 K Gas constant, Rc p c v Gas Formula kJ/kg·K kJ/kg·K kJ/kg·K k Air — 1005 0718 1400.
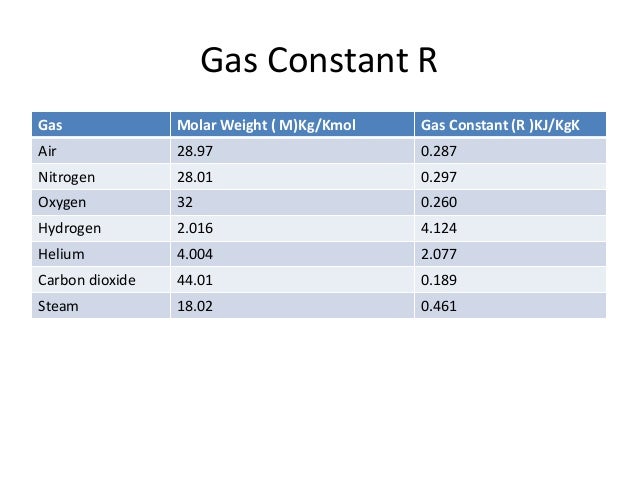
The ideal gas law states that PV/T is constant The pressure in the freezer is atmospheric pressure, the temperature in the freezer is lower that the outside temperature, so the volume of the balloon decreases when it is placed into the freezer Air is composed of 77% nitrogen, 21% oxygen and 2% other gases by weight The density of air at. Defines a specific gas constant with a value of 287 for air if Joule is chosen for the unit of energy, kg as unit of mass and K as unit of temperature, ie. T is the temperature of the gas, measured in Kelvins;.
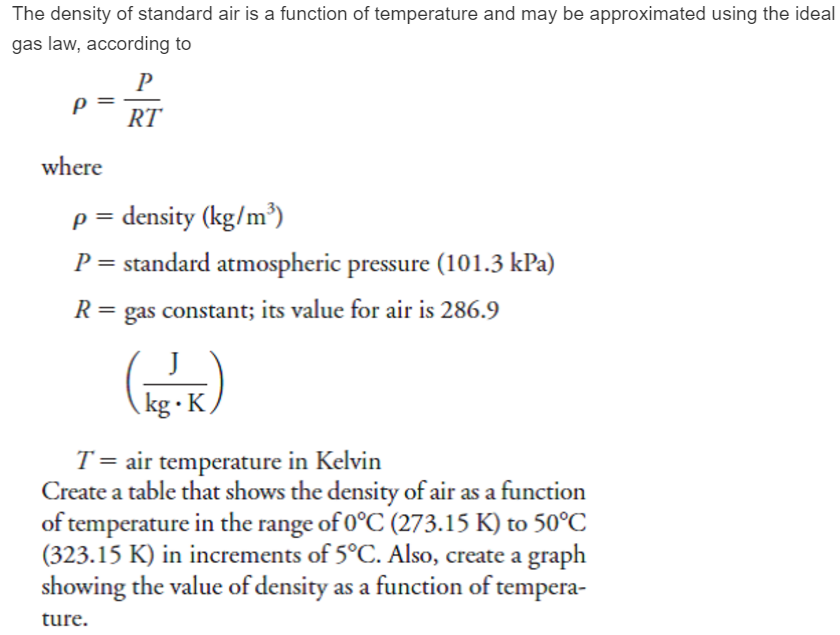
May 14, 15 · Notice that Universal Gas Constant version of the Ideal Gas Law is dependent on molarity (mol/m^3), as we do not know what gas is filling that space From the resulting moles we can now calculate the mass of a particular substance within that volume and change the equation to one of molality (mass dependent). May 23, 21 · Question 1) The density of air is to be betermined by using ideal gas equation P=PRT Ideal gas constant for air is given as R= 2871 J/kgK Temperature and pressure are measured as T= 328 45 K P= 125 05 kPa Determine the value of density, p and its uncertainity. Values of R (Gas Constant) Value Units (VPT −1n−1) 14 4621(75) J K−1 mol−1 51 × 1019 eV K−1 mol−1 00 057 46(14) L atm K−1 mol−1 1985 8775(34) cal K−1 mol−1 1985 8775(34) × 10−3 kcal K−1 mol−1 14 4621(75) × 107 erg K−1 mol−1 14 4621(75) L kPa K−1 mol−1 14 4621(75) m3 Pa K−1 mol−1.
May 28, 19 · The ideal gas constant is also known as the universal gas constant or the molar gas constant or simply the gas constant It is a very important constant in chemistry and physics It is denoted as R The dimension of the gas constant is expressed in. Analysis is used to study the open gas turbine engine with the assumptions that air is the working ideal gas and the energy generated by combustion is accomplished by a heat transfer For an ideal airstandard Brayton cycle, there are no frictional pressure drops, and the air flows at constant pressure through the heat exchangers The. May 22, 14 · The constant factor in the equation of state for ideal gases The universal gas constant, also known as the molar or ideal gas constant, is R* = (75) J mol 1 K 1 The gas constant for a particular gas is.
The ideal gas law can be derived from basic principles, but was originally deduced from experimental measurements of Charles’ law (that volume occupied by a gas is proportional to temperature at a fixed pressure) and from Boyle’s law (that for a fixed temperature, the product PV is a constant)In the ideal gas model, the volume occupied by its atoms and molecules is a. Ideal Gas Practice Problems Problem 1 Under normal conditions (temperature 0 °C and atmospheric absolute pressure 100 kPa), the air density is 128 kg/m³ Determine the average molar mass of air Solution From the given air density we know that the mass of one cubic meter of air is 128 kg Click the Reset button and enter the problem data into the calculator. May 23, 19 · where P is the pressure exerted by an ideal gas, V is the volume occupied by an ideal gas, T is the absolute temperature of an ideal gas, R is universal gas constant or ideal gas constant, n is the number of moles (amount) of gas Derivation of Ideal Gas Law The ideal gas law can easily be derived from three basic gas laws Boyle's law, Charles's law, and Avogadro's law.
Nov 07, 16 · Ideal gas law equation The properties of an ideal gas are all summarized in one formula of the form pV = nRT where p is the pressure of the gas, measured in Pa;;.

Metr 2413 11 And 13 February 04 Thermodynamics
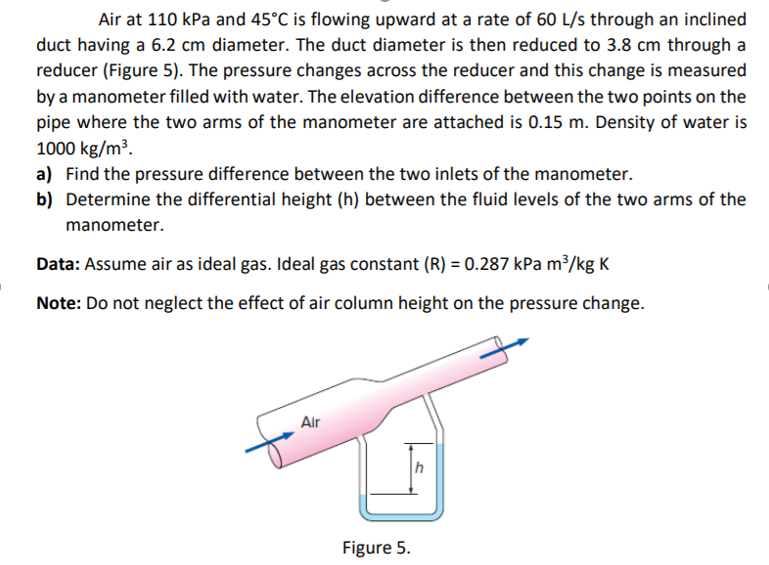
Answered Air At 110 Kpa And 45 C Is Flowing Bartleby
How To Calculate The Characteristic Gas Constant Of A Gas Air Quora
Air Ideal Gas Constant のギャラリー

Ideal Gas An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

How To Use Abaqus Cel To Model Air Pressure

Ideal Gas Laws Worked Problems On The Characteristic Gas Equation And Further Worked Problems On The Characteristic Gas Equation Hvac Machinery

The Ideal Gas Law Gas Constant Applications Of The Gas Law P R R T Lecture 2 Atmospheric Thermodynamics Pdf Free Download

Thermodynamics Gases Mole Unit

Equation Of State

The Ideal Gas Law The Bumbling Biochemist

Ideal Universal Gas Law Chemistrybytes Com

Volume And Mass Flow Calculations For Gases
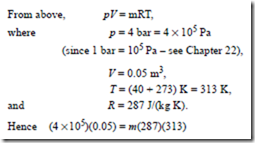
Ideal Gas Laws Worked Problems On The Characteristic Gas Equation And Further Worked Problems On The Characteristic Gas Equation Hvac Machinery

Solved This Question Relates To Thermodynamics Why Is R Chegg Com

Using The Ideal Gas Relationships

Ideal Gas Law

Speed Of Sound
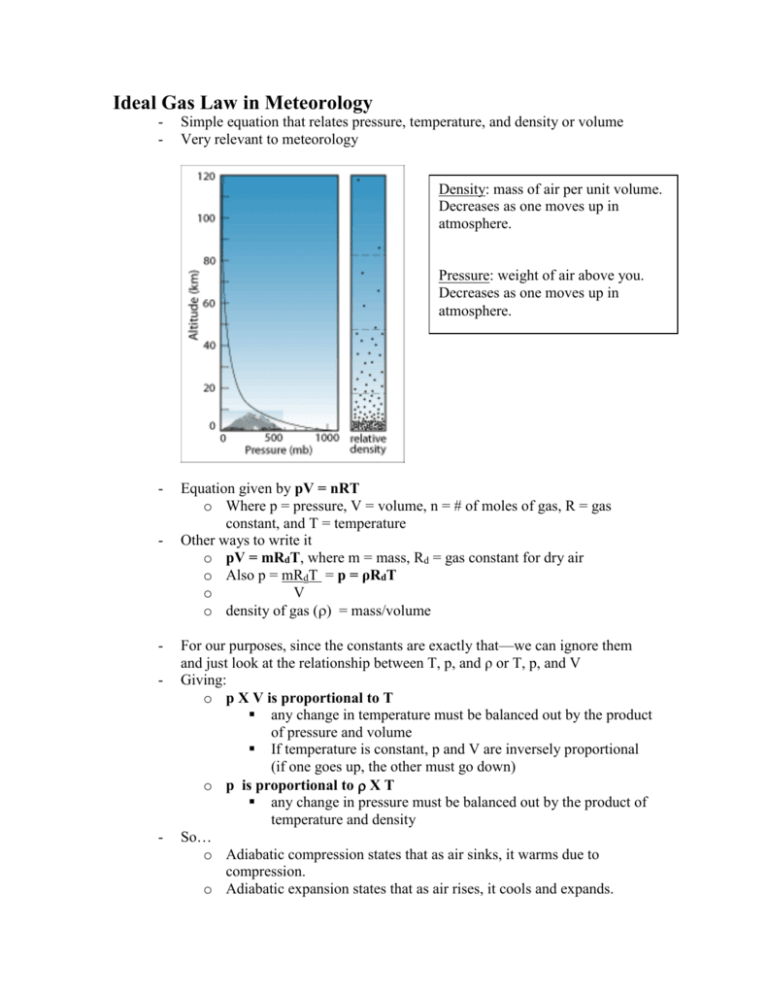
Ideal Gas Law In Meteorology
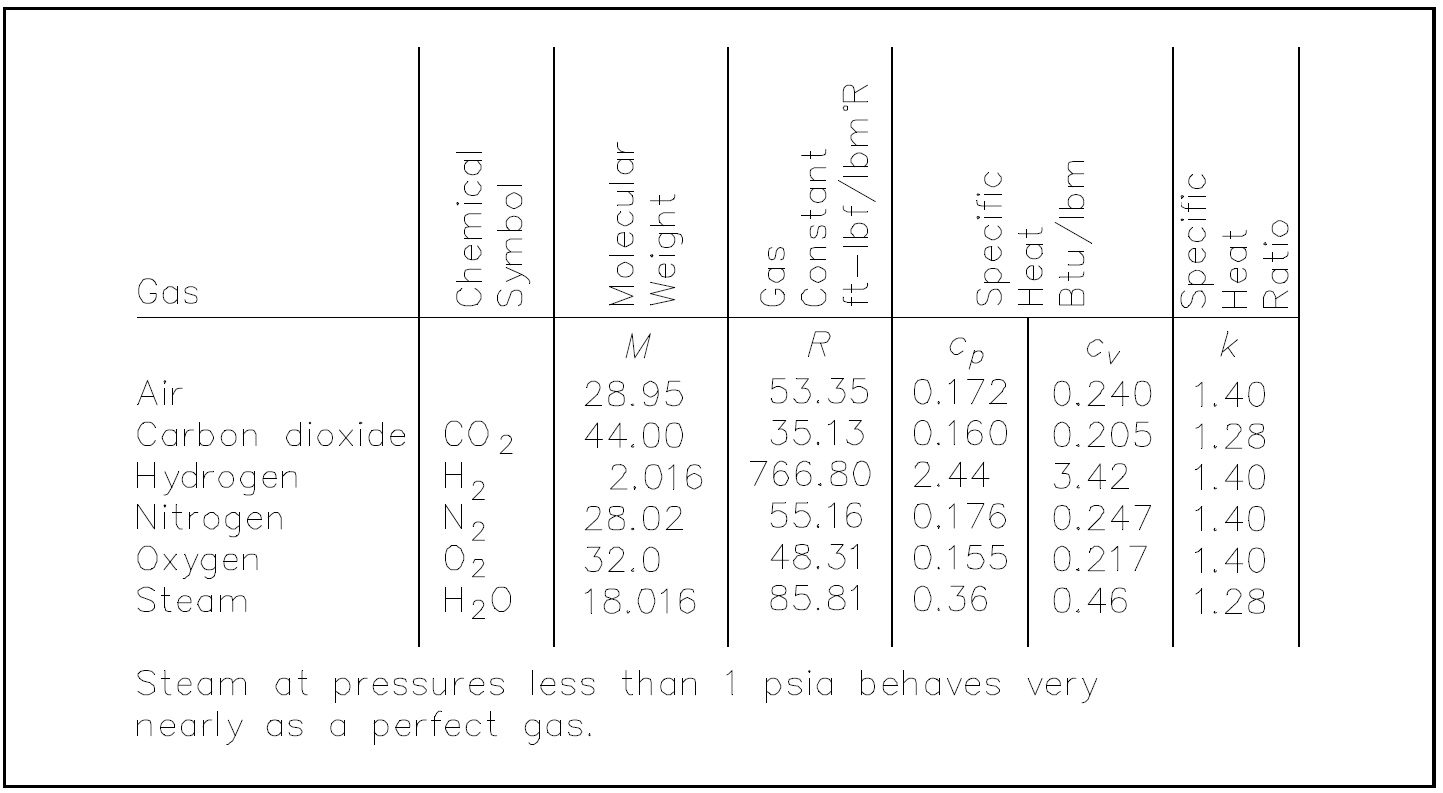
Thermodynamics Help Ez Pdh Com

A Hot Air Balloon Contains 85 000 Moles Of Air To What Temperature Must The Air Be Heated To Fill A Brainly In

L 14 Physics Of Dry Air And Moist
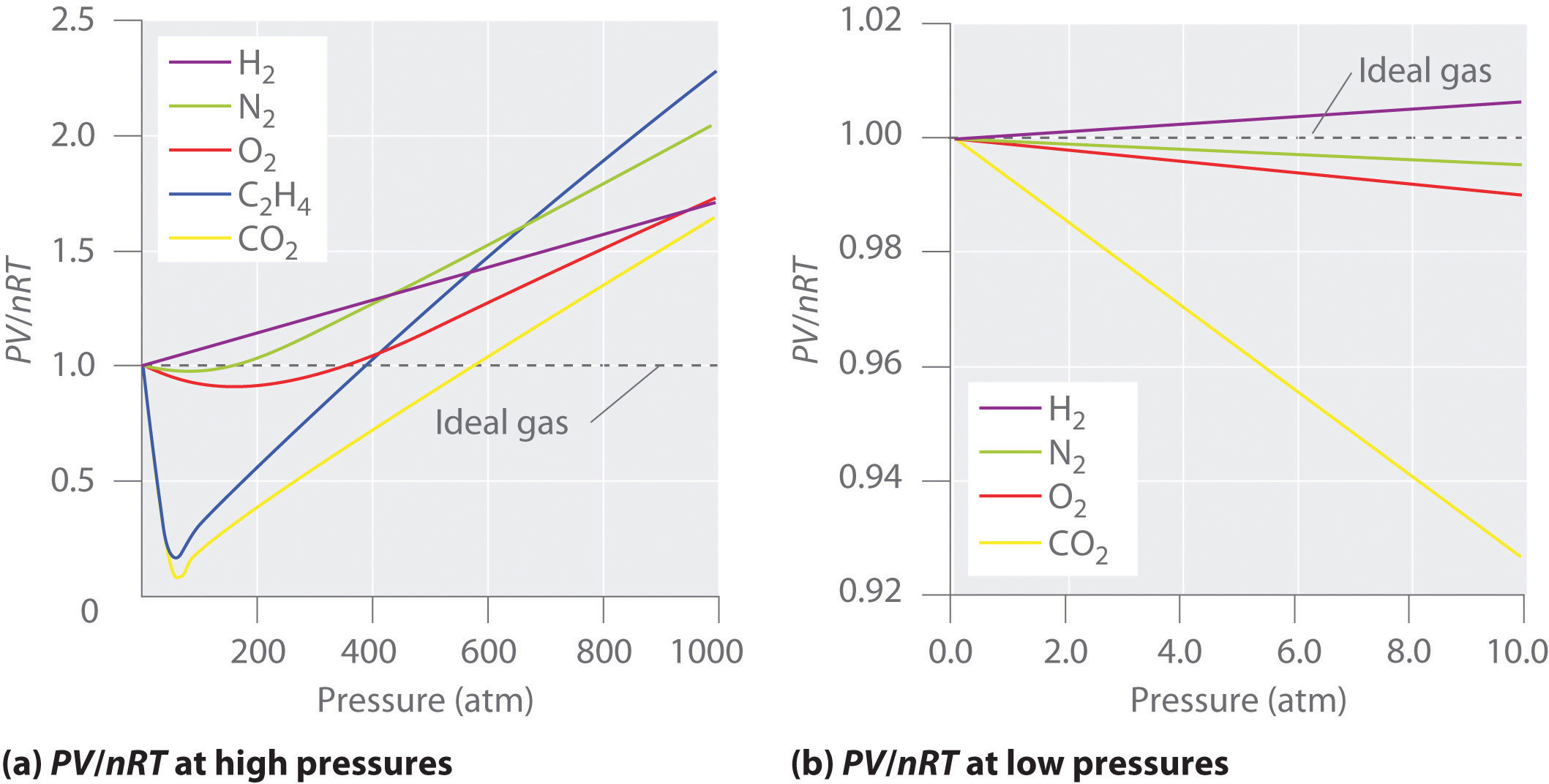
The Behavior Of Real Gases

Ppt Aos 101 Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id

Ideal Gas An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Ideal Gas Law Wikipedia

Deviations From Ideal Gas Law Behavior

Using The Ideal Gas Law To Calculate A Change In Volume Worked Example Video Khan Academy

How To Calculate Air Density
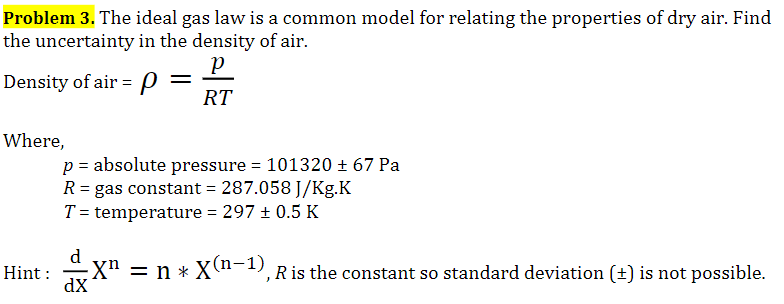
Solved Problem 3 The Ideal Gas Law Is A Common Model For Chegg Com

Derive The Air Mass Fraction Relation As Follows 2pt R Is Gas Constant For Steam R 0 4615 Kj Kg K For Air R 0 287 Homeworklib

Density Of Air Wikipedia
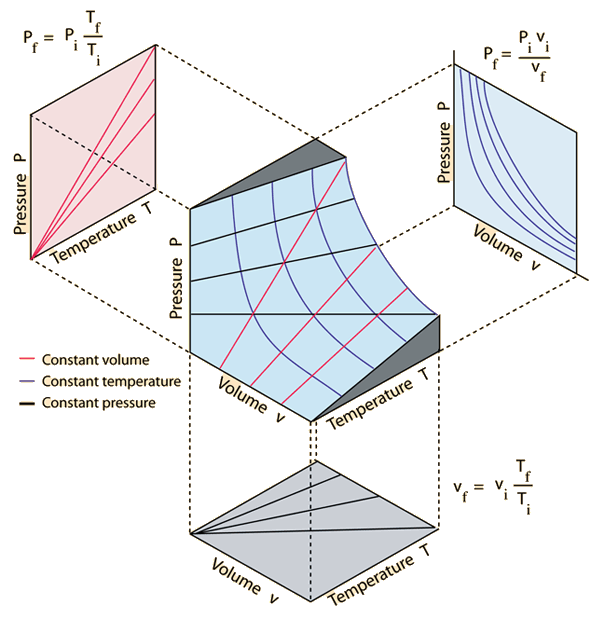
Ideal Gas Law

9 1 An Ideal Gas Flows Adiabatically Through A Duct At Section 1 P1

Ideal Gas Law Its Effects On Leak Testing Zaxis Inc

Introduction

Ideal Gas Law Calculator
Air Properties Of

Moisture Variables The Equation Of State For Moist Air Ppt Download
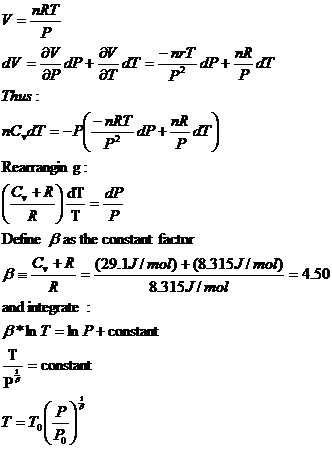
Meteorological Model
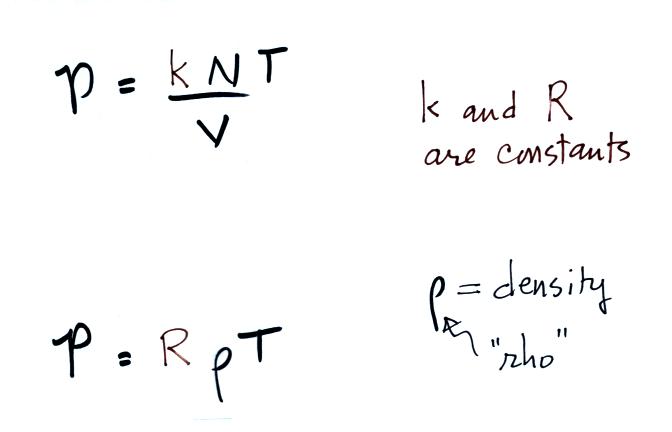
Lecture 6 Ideal Gas Law Rising And Sinking Air
Solved The Density Of Standard Air Is A Function Of Tempe Chegg Com

Air Properties Definitions

Balloon Power Energy Ideal Gas Law Power Energy Thermodynamics

Barometric Formula

Thermo Find Mass Of Air In A Room Find Mass Of Gas When Given Pressure Volume Gas Constant Temp Youtube
The Ideal Gas Equation

Dry Air Density In A Given Sample Of Moist Air The Dry Air Density Is Using The Ideal Gas Law The Molecular Weight Of Dry Air And Partial Pressures Back To Thunder S Home Page

Slides Show

Answered Answer The Following Questions Bartleby
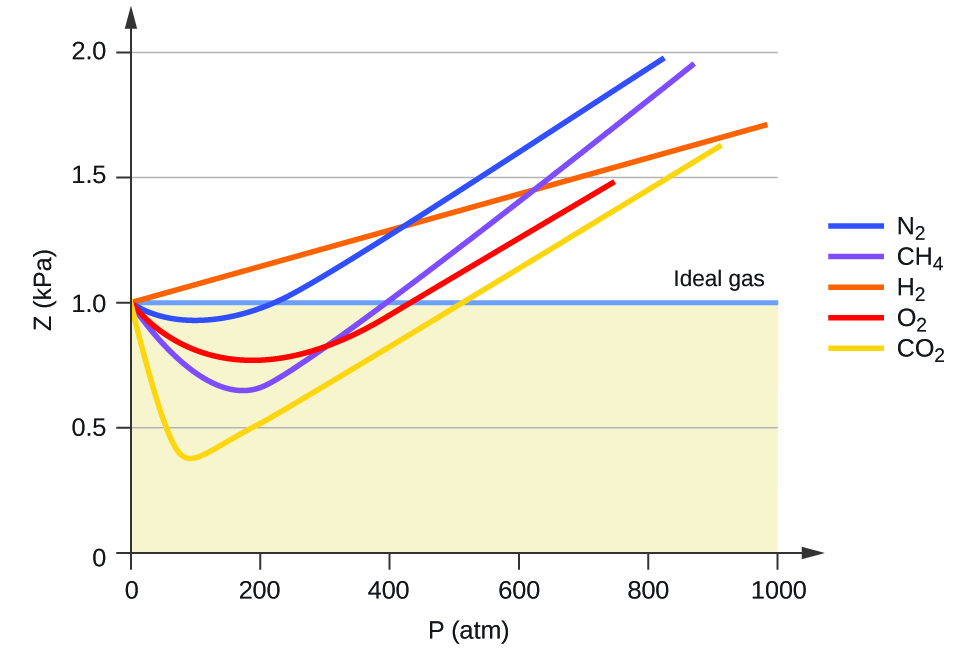
9 6 Non Ideal Gas Behavior Chemistry Libretexts

Phase Changes Of Water Gibbs Phase Rule

Solved 7 16 Employing The Ideal Gas Model Determine The Change In Transtutors
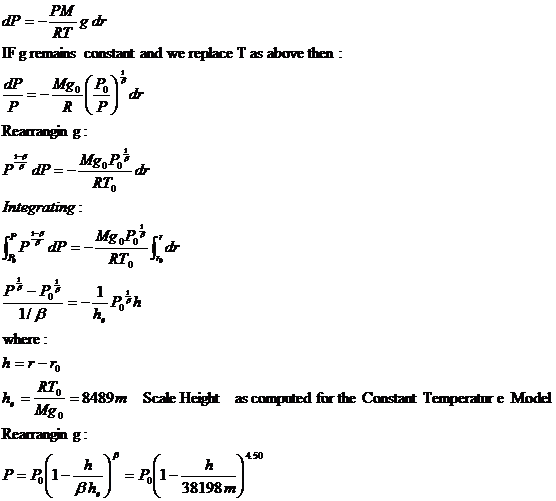
Meteorological Model
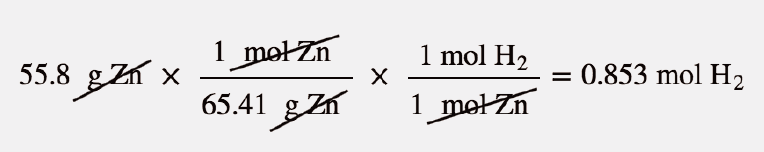
The Ideal Gas Law And Some Applications Introductory Chemistry 1st Canadian Edition
Lecture 6 Ideal Gas Law Rising And Sinking Air

Tire Pressure Math Math Encounters Blog
Ideal Gas Law

Ideal Gas Constant Definition Values And Units Chemistrygod
Calculate Enthalpy Change Of An Ideal Gas System Youtube

Lapse Rates Moisture And Clouds

Chapter 11 Combustion Updated 5 31 10

Ideal Gas Law Equation Constant Derivation Graphs Chemistrygod

The Ideal Gas Law The Bumbling Biochemist

Moisture Variables The Equation Of State For Moist Air So 254 Spring 17 Lcdr Matt Burich Slideshow And Powerpoint Viewer Ideal Gas Law Eqn Of State For Dry Air
01 Part2 Ideal Gas Problems 01

Why Sometimes We Can Find P Rgrt Instead Of P Rrt For Ideal Gas Physics Stack Exchange

ditional Ideal Gas Studocu

Chapter 2b Pure Substances Ideal Gas Updated 1 17 11

Real Gases Using The Van Der Waals Equation Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
Equation Of State

Slides Show
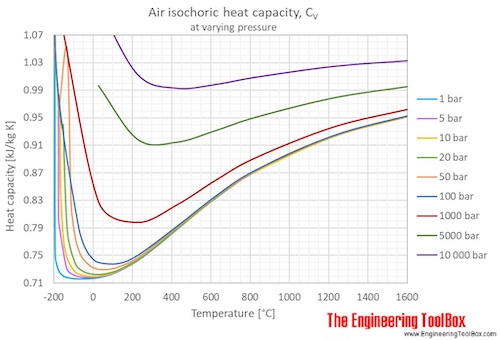
Air Specific Heat At Constant Pressure And Varying Temperature

Air Pressure Density And Temperature Vs Altitude In Standard Atmosphere Calculator Thermodynamics Heat Online Unit Converters

Lesson Worksheet The Ideal Gas Law Nagwa
The Ideal Gas Law And Some Applications Introductory Chemistry 1st Canadian Edition
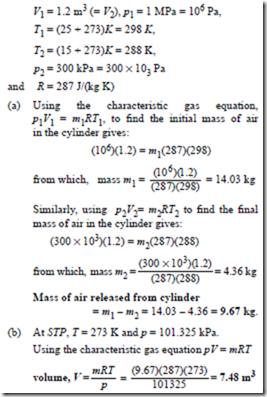
Ideal Gas Laws Worked Problems On The Characteristic Gas Equation And Further Worked Problems On The Characteristic Gas Equation Hvac Machinery
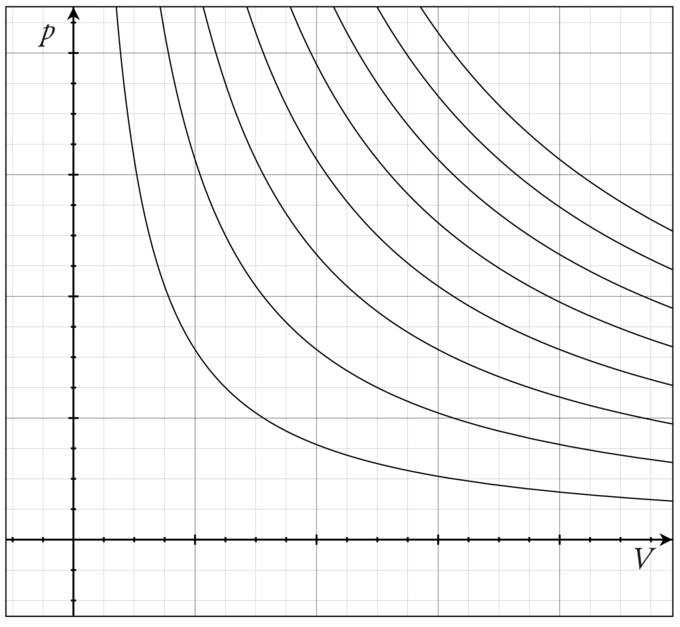
Ideal Gas Law Boundless Physics

Figure 7 From Ideal Gas Effects In Aeroacoustics Jerin Semantic Scholar

Composition Of Dry Air Download Table
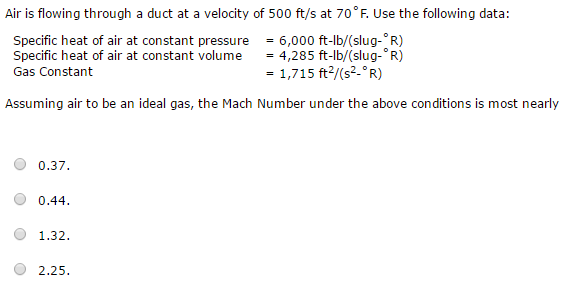
Solved Air Is Flowing Through A Duct At A Velocity Of 500 Chegg Com
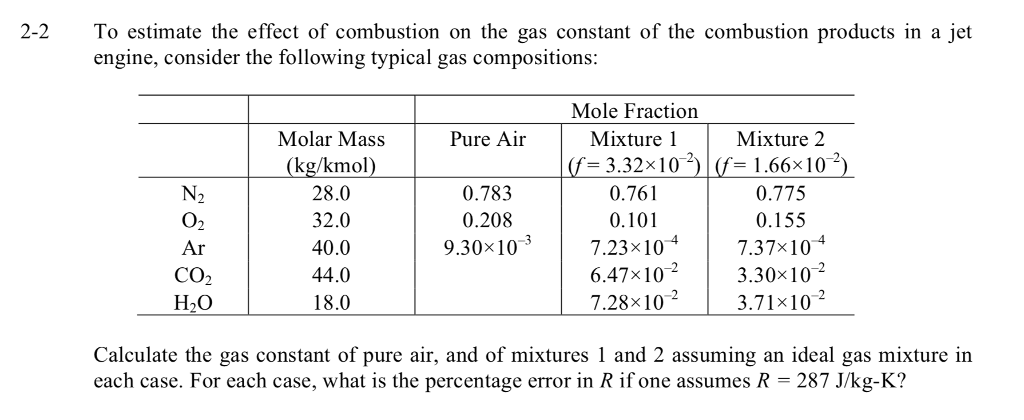
Solved 2 2to Estimate The Effect Of Combustion On The Gas Chegg Com
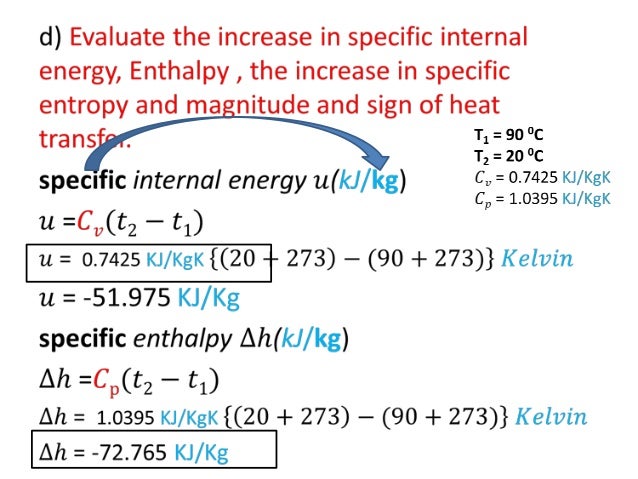
01 Part2 Ideal Gas Problems 01

Ppt Atmospheric Thermodynamics Part I Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id

Go To Oldcoursework Com To Get Your Answers

Psychrometric Properties Of Moist Air Ppt Download

Ideal Gas Law Application To Air Gases Pressure
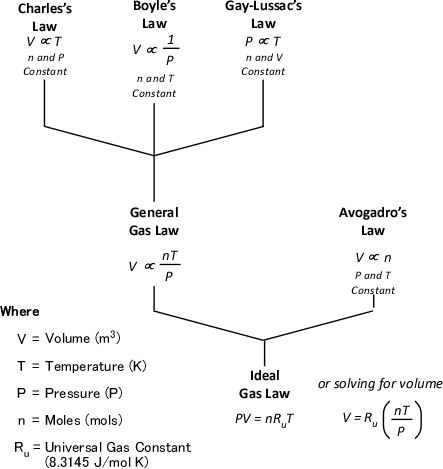
Blog Archive Gas Cooling Part 4 Compartment Fire Behavior

What Value Of R Gas Constant Should Be Used Quora

01 Part2 Ideal Gas Problems 01

Using The Ideal Gas Law To Calculate Number Of Moles Worked Example Video Khan Academy




